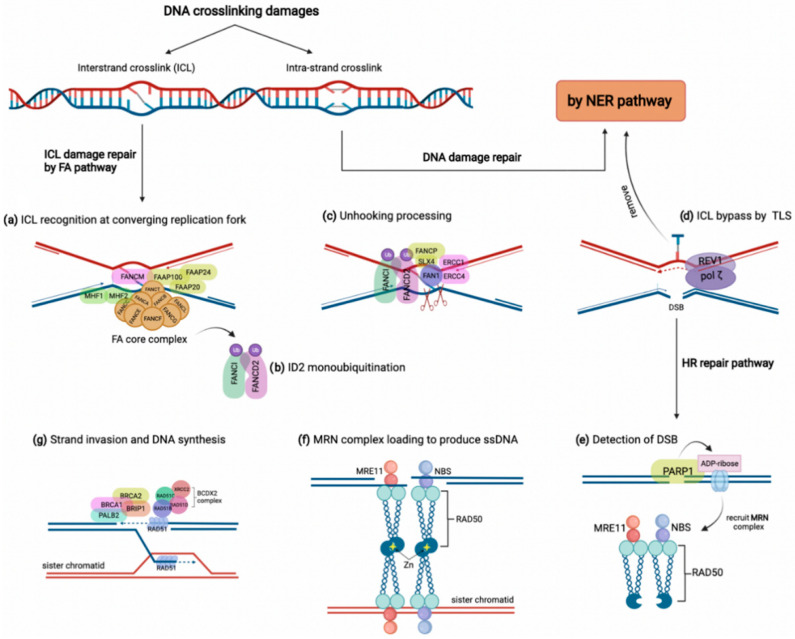
Figure 1.
The FA pathway and inter-strand crosslink (ICL) repair. DNA crosslinking damages generally include intra-strand and inter-strand crosslink damages, which are repaired by NER and FA pathways, respectively. (a) In the FA pathway, the ICL damage is recognized by FANCM accompanying some other FAAPs at converging replication fork, which results in FA core complex loading along with FAAP100, FAAP20, and FAAP24, as well as MHF1 and MHF2. (b) FA core complex activates the ID2 complex by monoubiquitylation of FANCI and FANCD2. (c) Monoubiquitylated ID2 complex activates several endonucleases, such as FAN1, to stimulate unhooking processing of the ICL. (d) The unhooked ICL is removed by the NER pathway and bypassed by translesion synthesis polymerases REV1/pol ζ. (e,f) The HR pathway is recruited to repair the DSB on the other strand. After detection of DSB by PARP1, ADP-ribose molecules recruit the MRN complex to produce single-strand DNA and bind sister chromatid through a tail-to-tail link with another MRN complex. (g) Some FA members, such as BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, and PALB2, in addition to the BCDX2 complex, induce the attachment of FANCR/RAD51 to ssDNA, which promotes strand invasion and DNA synthesis.