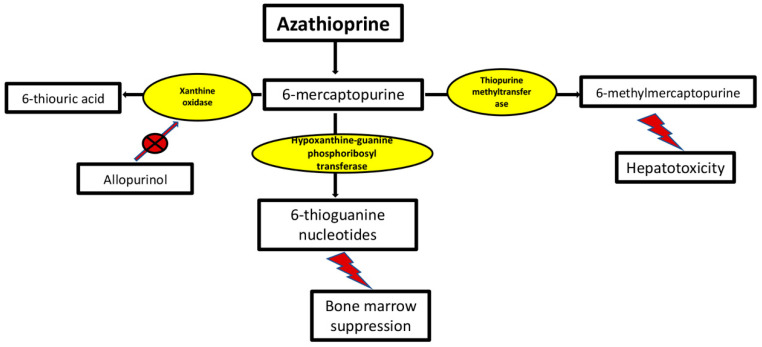
Figure 1.
Azathioprine metabolism. Deficiency of thiopurine methyltransferase results in increased 6-thioguanine levels, which may result in myelosuppression. On the other hand, increased activity of thiopurine methyltransferase will lead to increased levels of 6-methylmercaptopurine, which predisposes to hepatotoxicity (hypermethylation). Allopurinol can result in severe leukopenia if administered with the usual dose of azathioprine as it inhibits xanthine oxidase.