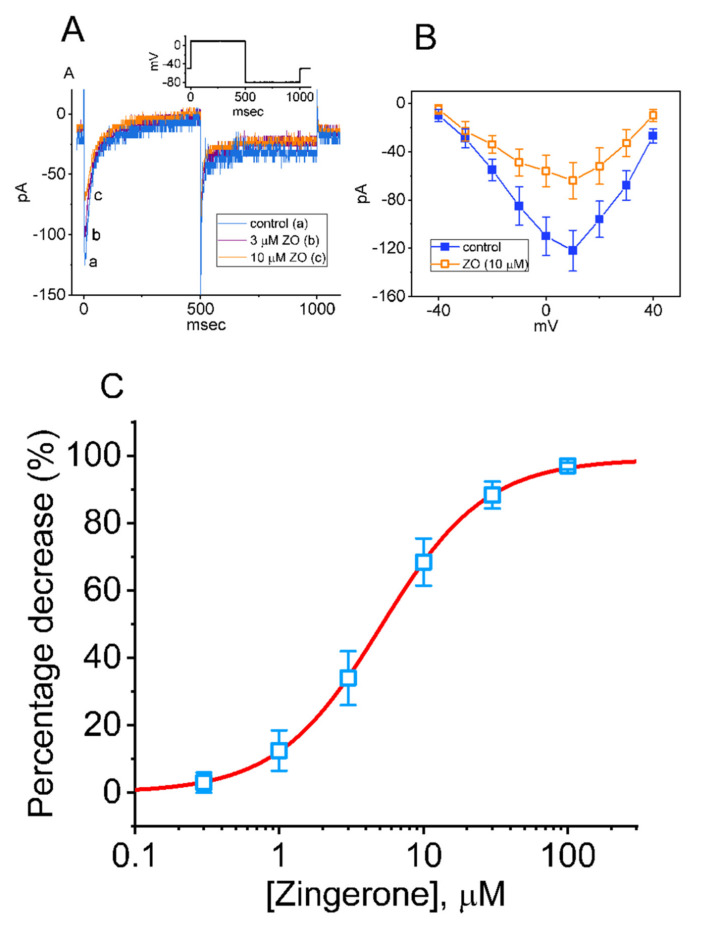
Figure 3.
Inhibitory effect of ZO on the L-type Ca2+ current (ICa,L) identified in GH3 cells. In these experiments, the cells were kept immersed in a normal Tyrode’s solution containing 1.8 mM CaCl2. The recording electrode was filled with Cs+-containing solution. (A) Representative current traces obtained under (a) the control situation (i.e., ZO was not present), and in the presence of 3 μM ZO (b) or 10 μM ZO (c). The inset shows the applied voltage-clamp protocol. (B) Mean current vs. voltage (I–V) relationships of peak ICa,L in the absence (■) and presence (□) of 10 μM ZO (mean ± SEM; n = 7 for each point). The current amplitude was measured at the start of each membrane depolarization to voltages ranging between −40 and +40 mV from a holding potential of −50 mV. (C) Concentration-dependent effect of ZO on the amplitude (□) of ICa,L evoked by membrane depolarization to +10 mV from a holding potential of −50 mV (mean ± SEM; n = 8 for each point). The current amplitude was measured at the start of the depolarizing pulse during exposure to various concentrations of ZO. The continuous smooth line indicates the goodness-of-fit to the modified Hill equation, as stated in the Section 4.