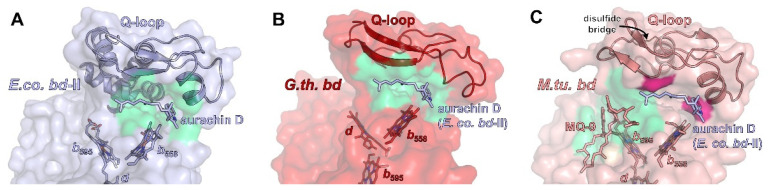
Figure 3.
Quinol binding sites in bacterial bd oxidases. (A) Quinol binding site in E. coli bd-II (pdb ID 7OSE). The specific inhibitor aurachin D is shown as sticks, the interacting surface of CydA is shown in green, the residual protein surface in light blue. The Q-loop is involved in binding and provides the top half of the binding site. (B) Aurachin D (modelled from 7OSE after superimposing 5DOQ and 7OSE) perfectly fits to the putative quinol binding site in G. thermodenitrificans (5DOQ, green surface, residual protein surface given in red). (C) The corresponding cleft below the Q-loop in mycobacterial bd oxidases (shown for M. tuberculosis) is too narrow for aurachin D (putative clashes shown in hotpink). Instead, a quinol binding site was identified close to heme b595, where menaquinone-9 was found to interact with CydA (green surface, residual protein surface in light salmon).