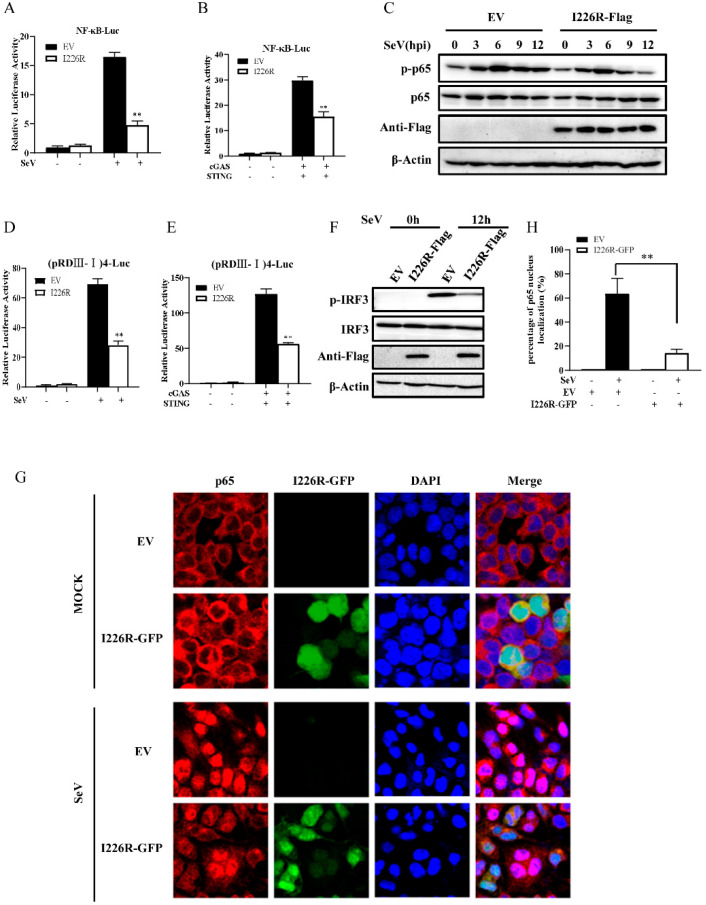
Figure 5.
The I226R protein impairs the activation of NF-κB and IRF3 signaling: (A) 500 ng NF-κB-Luc, 50 ng pRL-TK, and 500 ng I226R-Flag or EV were co-transfected with 293T cells for 24 h and infected with SeV for 16 h. The NF-κB luciferase activity was measured. (B) 300 ng NF-κB-Luc, 30 ng pRL-TK, and 300 ng I226R-Flag or EV were co-transfected in 293T cells for 24 h with 300 ng cGAS-Flag and 50 ng STING-HA. The NF-κB luciferase activity was measured. (C) 293T cells were transfected 3 μg I226R-Flag or EV for 24 h and infected with SeV for indicated time. Western blotting was performed to detect the phosphorylation levels of p65. (D) 500 ng (pRDIII-I)4-Luc was used instead of NF-κB-Luc, as described in panel A. The IRF3 luciferase activity was measured. (E) 300 ng (pRDIII-I)4-Luc was used instead of 300 ng NF-κB-Luc, as described in panel B. The IRF3 luciferase activity was measured. (F) 293T cells were transfected with 3 μg I226R-Flag or EV and infected with SeV for 12 h. Western blotting was then performed to detect the phosphorylation levels of IRF3. (G,H) 293T cells were transfected with 3 μg I226R-GFP or EV and infected with SeV for 12 h. The cells were stained with anti-p65 Ab. Alex Fluor 594-conjugated IgG (red) was used as the secondary antibody. Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). The images were obtained by laser scanning confocal microscope using a 20× objective (G). Quantification of the nuclear translocation of p65 was determined by counting 100 cells from at least three independent fields (H). Shown are percentages of cells with p65 located in the nuclei. The results are expressed as the means ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using the Student’s t-test. ** p < 0.01.