Figure 5.
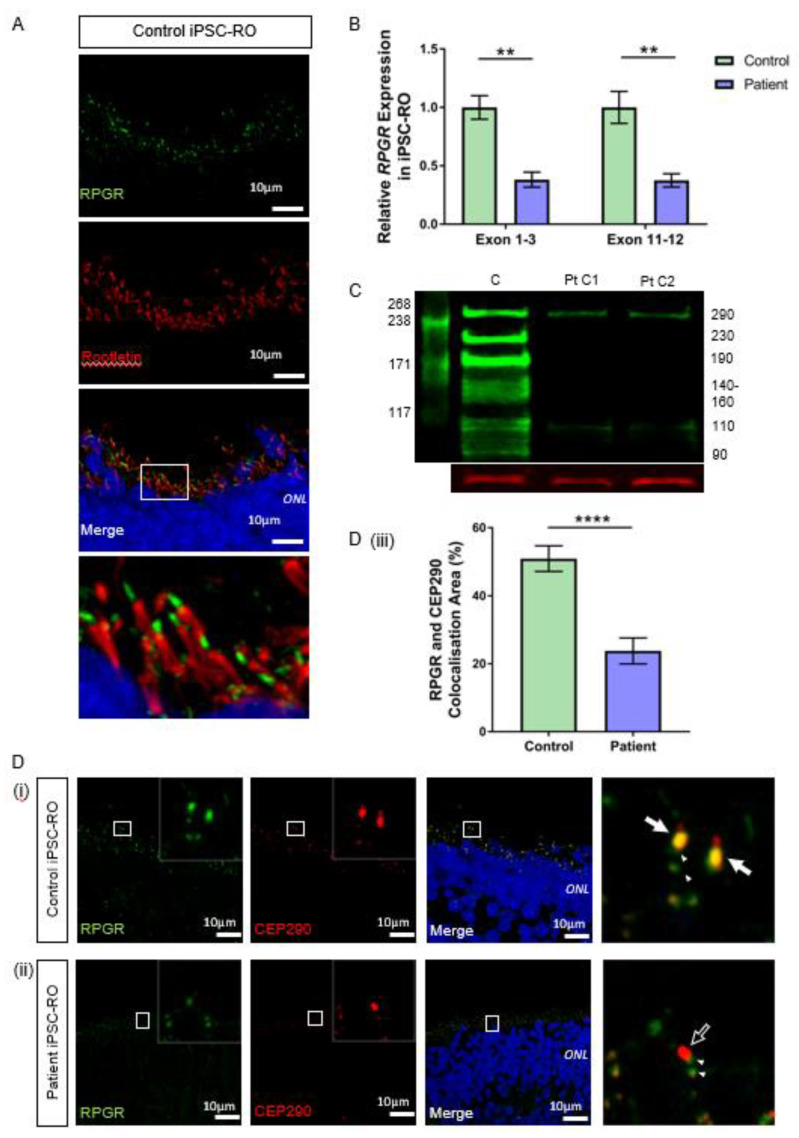
RNA and protein studies in RPGR c.1415 − 9A>G variant iPSC-ROs. (A) Normal localisation of RPGR was shown to be distal to rootletin staining. Rootletin marks the base of the primary cilia, so in the photoreceptor cells of the retinal iPSC-ROs, RPGR is localising to the transitional zone of the cilium. (B) The expression of RPGR determined by RT-qPCR was decreased in patient iPSC-ROs (30 weeks) compared to control cells at exon 1-3 and exon 11-12 (unpaired t-test, ** p < 0.01; SEM from n = 4 independent experiments, mRNA extracted from n = 5 pooled iPSC-ROs per experiment per line). Expression levels are relative to both HPRT and POLR2A housekeeper genes. (Control = Controls 1 and 2; Patient = Clones 1 and 2). (C) A western blot analysis of control (C) iPSC-ROs revealed multiple bands typical of RPGR (green). Patient (Pt C1; Pt C2) iPSC-ROs showed a reduction in 290 kDa and 110 kDa bands, with a loss of bands at 230 kDa, 190 kDa, 140–160 kDa, 125 kDa and 90 kDa. Vinculin (red) was used as a loading control. (Control = Controls 1 and 2; Patient = Clones 1 and 2; n = 4 individual experiments). (D) Control iPSC-RO and patient iPSC-RO photoreceptor cells at an age of 30 weeks were stained with antibodies against RPGR (green) and CEP290 (red), which localizes mainly to the TZ of photoreceptor cilia. (i) Control iPSC-ROs showed strong yellow co-staining (white arrow) along the ciliary TZ (Control = Control 1). (ii) Patient iPSC-ROs showed a lack of RPGR staining and hence a lack of co-staining with CEP290 at the photoreceptor TZ (white arrow outline). In both the control and patient cells, there was a presence of RPGR staining just away from the TZ region, which may be consistent with the localization in the basal bodies (green punctate staining denoted by white arrowheads). (Patient = Clone 2). (iii) An image analysis using ImageJ verified that control photoreceptor cilia have a larger overlapping area in the yellow co-staining of CEP290 with RPGR, whereas in patient cilia, this is lost (unpaired t-test, **** p < 0.0001; SEM from n = 4 independent iPSC-ROs per line). The co-localisation area was normalised against the CEP290 area and expressed as a percentage. (Control = Control 1 and 2; Patient = Clones 1 and 2).