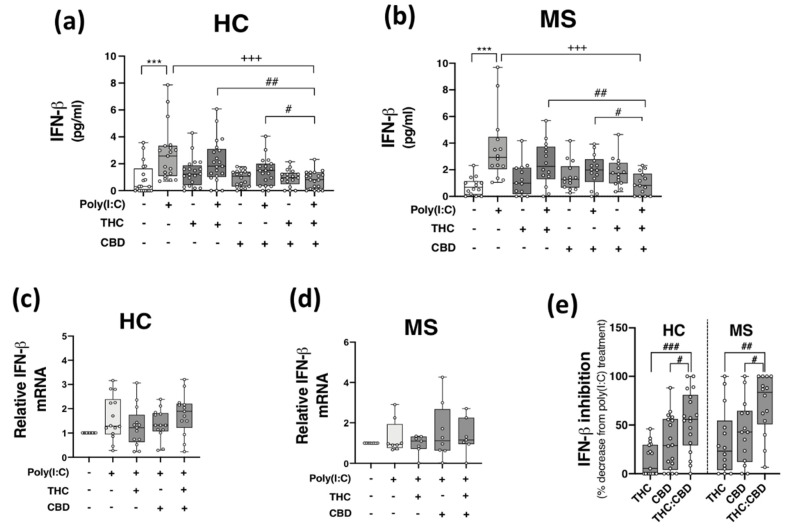
Figure 3.
THC:CBD inhibits TLR3-induced IFN-β protein expression in PBMCs from HC subjects and pwMS. Treatment of PBMCs from (a) HCs and (b) pwMS with poly(I:C) (10 μg/mL; 24 h) increased IFN-β protein expression. Pre-treatment with THC (10 μM) and CBD (10 μM) in combination (1:1) (45 min pre-treatment) significantly inhibited poly(I:C)-induced IFN-β protein expression in PBMCs from (a) HCs (Kruskal–Wallis statistic = 30.4) and (b) pwMS (Kruskal–Wallis statistic = 30.3). Effect of poly(I:C), THC (10 μM) and CBD (10 μM) treatment on IFN-β mRNA expression in PBMCs from (c) HCs (Kruskal–Wallis statistic = 30.4), and (d) pwMS (Kruskal–Wallis statistic = 1.1). (e) Summary of the inhibitory effect of THC (10 μM), CBD (10 μM) and THC:CBD (10 μM:10 μM) on TLR3-induced IFN-β protein expression in PBMCs from HCs and pwMS (expressed as % decrease from poly(I:C) treatment). Treatment of PBMCs from HCs with THC:CBD (10 μM:10 μM) in the presence of poly(I:C), significantly inhibited IFN-β protein expression when compared to PBMCs treated with poly(I:C) + THC (10 μM) and poly(I:C) + CBD (10 μM) (Kruskal–Wallis statistic = 27.1). Treatment of PBMCs from pwMS with THC:CBD (10 μM:10 μM) in the presence of poly(I:C), significantly inhibited IFN-β protein expression when compared to PBMCs treated with poly(I:C) + THC (10 μM) and poly(I:C) + CBD (10 μM) (Kruskal–Wallis statistic = 27.1). Statistical significance was determined by Kruskal–Wallis tests, with Dunn’s multiple comparison post-hoc test to compare means of preselected pairs of groups. Data are presented as median IFN-β expression/inhibition, minimum and maximum values and IQR. Symbols indicate individual data points in PBMCs from 21 HCs and 14 pwMS for protein analysis, and 15 HCs and 8 pwMS for mRNA analysis. *** p < 0.001 versus vehicle control group. +++ p < 0.001 compared to cells treated with poly(I:C). # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 and ### p < 0.001 vs. PBMCs treated with poly(I:C) in the presence of THC:CBD in a 1:1 combination.