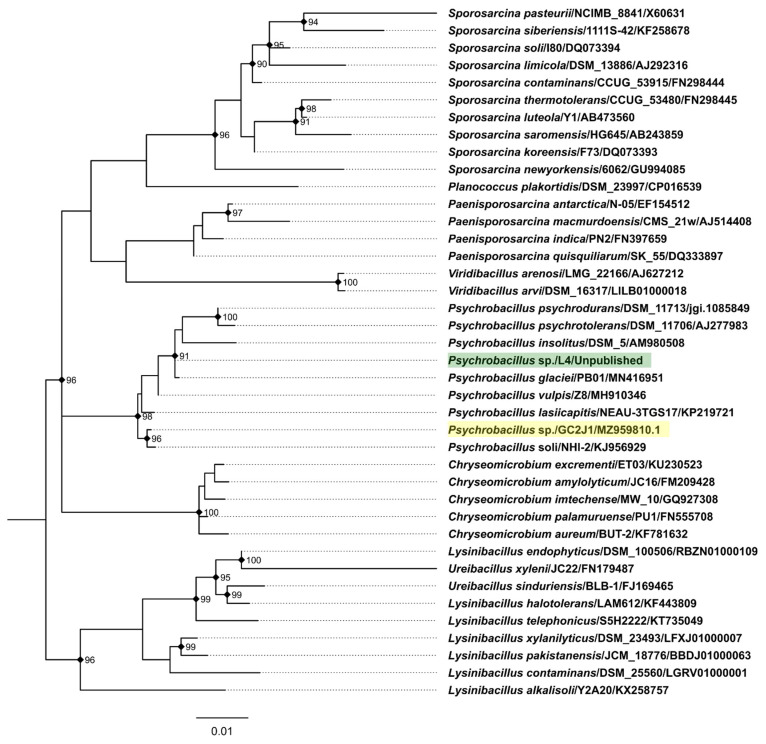
Figure 1.
Maximum likelihood phylogeny of the partial 16S rRNA gene sequences of Psychrobacillus isolate L4 (host of phages Perkons and Spoks; tip label highlighted in green; sequence obtained using common 27F and 1492R primers), Psychrobacillus isolate GC2J1 (host of phage PVJ1; tip label highlighted in yellow) and validly named closely related bacterial isolates found in the EzBioCloud database [5]. Clustal-Omega v.1.2.4 [6] was used in auto mode for the multiple sequence alignment (MSA), which was then restricted to informative positions only using Gblocks [7] under default settings, resulting in the MSA of 40 sequences and 1250 positions (148 parsimony-informative, 87 singleton sites, 1015 constant sites). Maximum likelihood phylogeny reconstruction was performed using IQTREE v2.0.6. [8] under K2P+R2 as the best-fit substitution model according to ModelFinder [9] while allowing for polytomies. Ultrafast bootstrapping (UFBoot [10]; 1000 replicates) was used to assess the node support. The tree is midpoint rooted and drawn to scale; branch lengths are in the unit of nucleotide substitutions per site. UFBoot support percentages are given for nodes having a support of more than 90%; these are also indicated by black rectangles. Tip labels are in the form of “Species/Strain/Accession”.