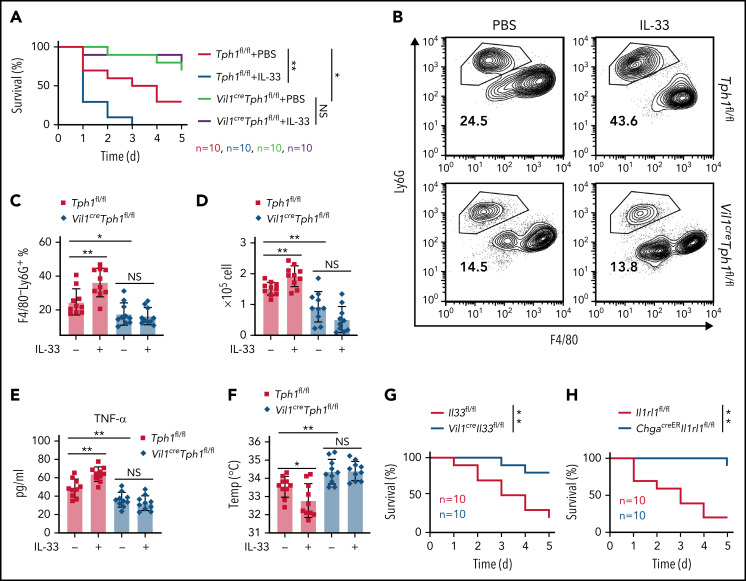
Figure 6.
IL-33 reduces survival of LPS endotoxic shock via peripheral 5-HT. (A-F) Intraperitoneal injection of E coli serotype 055:B5 LPS into Tph1fl/fl and Vil1creTph1fl/fl mice with or without IL-33 treatment. (A) Survival rate after LPS injection. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of lymphocytes isolated from peritoneum 4 hours after LPS injection. (C) Quantification of percentile of gated F4/80−Ly6G+ neutrophils in panel B. (D) Quantification of F4/80−Ly6G+ neutrophils isolated from peritoneum 4 hours after LPS injection. (E) Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) levels in the serum at 24 hours after LPS injection. (F) Body temperature was measured at 4 hours after LPS injection. (G-H) Intraperitoneal injection of E coli serotype 055:B5 LPS into Il33fl/fl and Vil1creIl33fl/fl mice (G) or Il1rl1fl/fl and ChgacreERIl1rl1fl/fl mice (H). Survival rate after LPS injection was monitored. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments (B) or are pooled from 2 independent experiments (A, C-H). *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 by Student t test. Error bars represent standard deviation. IFN-γ, interferon-γ; NS, not statistically significant.