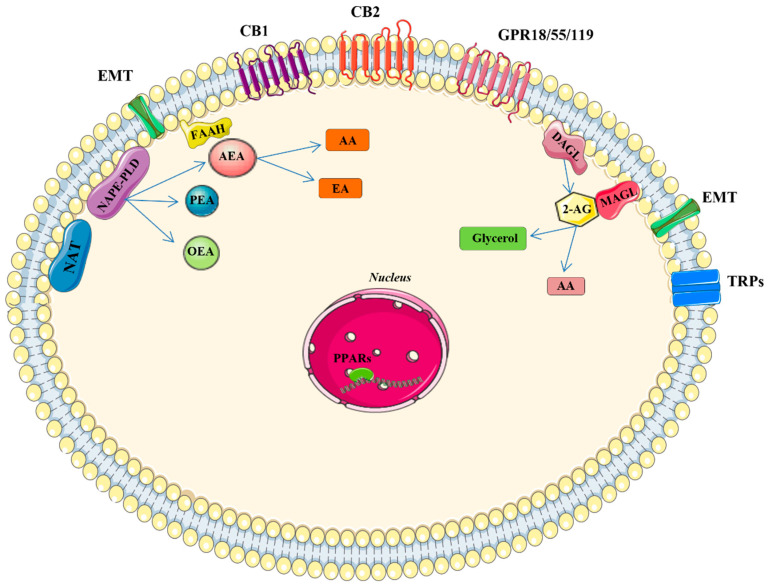
Figure 1.
Main components of the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Biosynthesis of AEA and 2-AG take place on demand from membrane phospholipids by NAPE-PLD or calcium-dependent NAT and DAGL, respectively. The reuptake of endocannabinoids into cells occurs across the cell membrane by putative endocannabinoid protein transporters (EMT). FAAH is the main enzyme responsible for AEA degradation, while MAGL is the key enzyme in the hydrolysis of the 2-AG releasing arachidonic acid. Receptor targets of AEA and 2-AG on the plasma membrane are various: CB1, CB2, GPR18, GPR55, GPR119, and TRPs and in the nucleus PPARs. Abbreviations: EA: ethanolamine; AA: arachidonic acid; CB1: cannabinoid receptor 1, CB2: cannabinoid receptor 2, TRPs: transient receptor potential channels (V1-3, A1, and M8 types). GPRs: G-protein-coupled receptor (18, 55, and 119), and PPARs: peroxisome proliferator-activated nuclear receptors α, γ, or δ; PEA: palmitoylethanolamide; OEA: oleoylethanolamide.