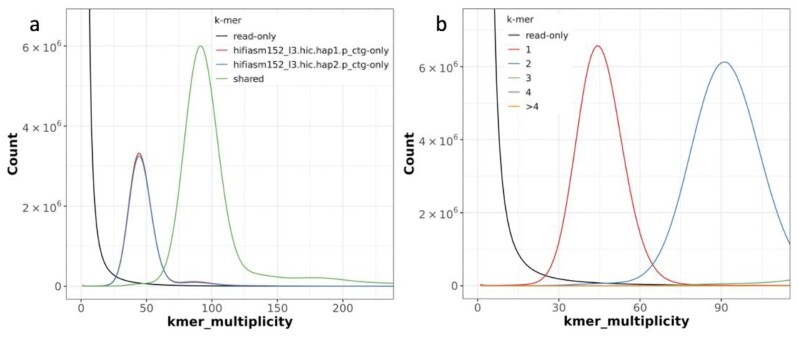
Figure 2:
Merqury assembly and copy number spectrum plots of cassava TME204 haplotigs. (a) For the Merqury assembly plot, k-mers are colored by their uniqueness in the Illumina PE reads (black), haplotype 1 (red) and haplotype 2 (blue) assemblies. Shared k-mers are shown in green. At the heterozygotes peak (45×), the second haplotype has only slightly fewer k-mers (blue) compared to the first haplotype (red), indicating that the reconstruction of heterozygous variants was almost complete. Red hump and blue shoulder ∼90× are haplotype-specific k-mers that are actually from homozygotes sequences, green shoulder ∼45× is due to shared k-mers belonging to heterozygotes. These shoulders are all very small, suggesting a very low level of collapsed homozygous regions and artificial duplications. (b) In the copy number spectrum plot, the majority of heterozygous k-mers appear once (red peak at 45×) and the majority of homozygous k-mers twice (blue peak at 90×), confirming that the assembly is close to complete haplotype-resolved and even the homozygous part of the genome is included in both haplotypes. High k-mer completeness is supported by the lack of black humps at 45× or 90×. Low artificial duplication is revealed by the barely detectable humps (green, purple, orange) of duplicated k-mers. The bars at zero k-mer multiplicity are low in both plots, suggesting that most k-mers in the assemblies are also present in Illumina reads and therefore the assembled sequences are of high consensus accuracy.