Fig. 1. Effect of intolerant score on general intelligence measured for deletions and duplications.
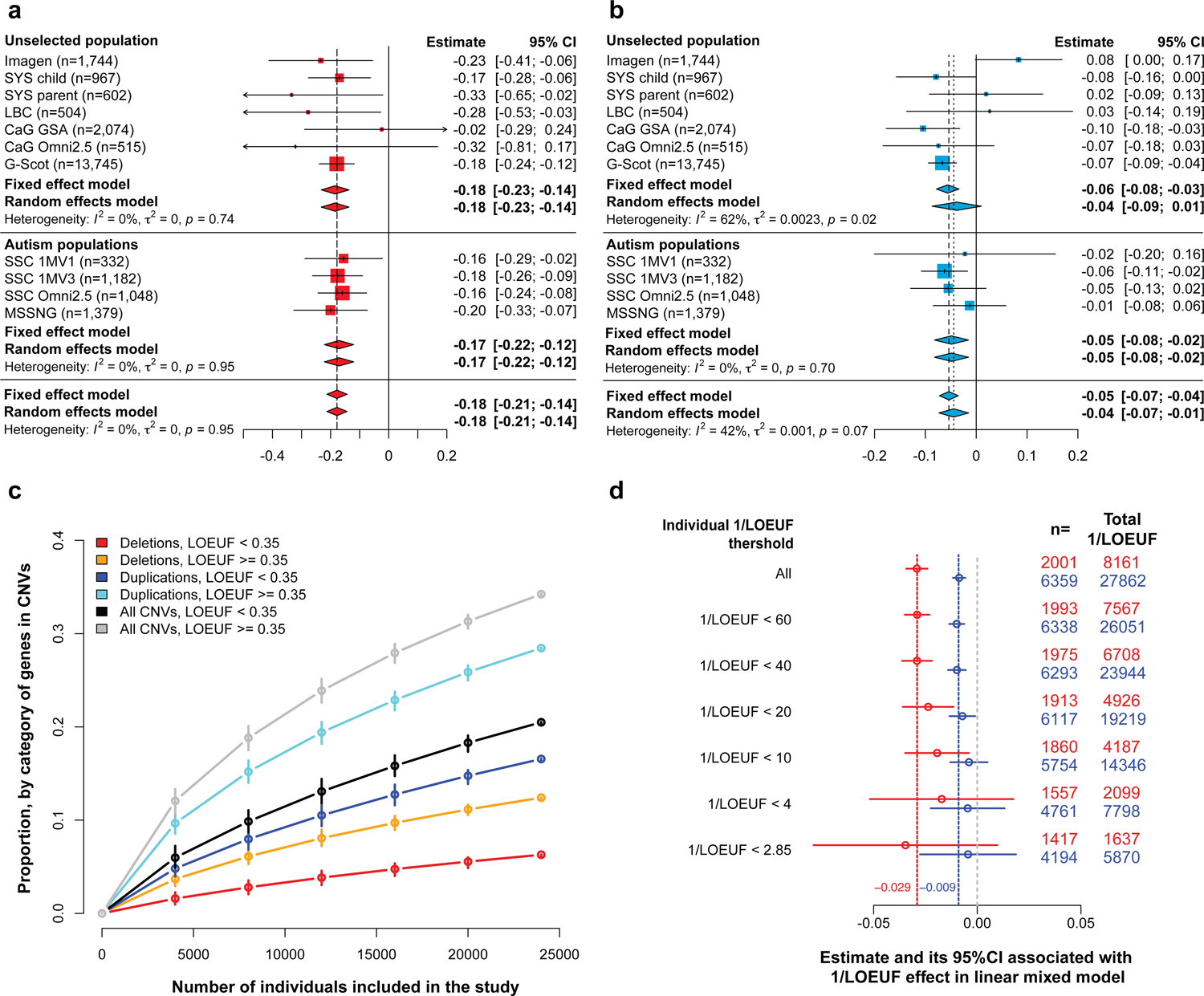
Meta-analysis estimating the effect of deletions a. and duplications b., measured by sum of pLI, on general intelligence (Supplementary Table 3). X-axis values represent z-scores of general intelligence. Deleting one point of pLI decreases the general intelligence by 0.18 z-scores (2.7 points of IQ). Duplicating one point of pLI decreases the general intelligence by 0.05 z-scores (0.75 points of IQ). The squares represent the effect-size computed for each sample. Their size negatively correlated to variance. Diamonds represent the summary effect across cohorts. Their lengths correspond to the 95% confidence intervals of the mean effect-size. c. Estimated proportion of the coding genome within each category defined by LOEUF, encompassed in CNVs present in the mega-analysis according to sample size (randomly selected within the mega-analysis). We observed NCNVs gene=6,315 with NDel. gene=2,282 and NDup. gene=5,223). d. Estimated effect of 1/LOEUF on general intelligence after removing individuals with a sum of 1/LOEUF larger than 60, 40, 20, 10, 4 and 2.85 (2.85 corresponds to 1/0.35, the cut-off for intolerance to pLoF gnomAD). n: number of individuals with a total sum of 1/LOEUF > 0.
