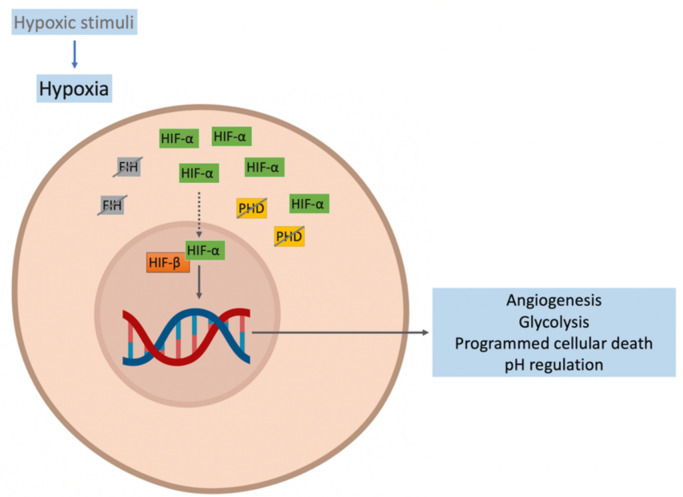
Figure 1.
Response to hypoxia. The activity of the prolyl hydroxylase domain (PHD) and factor-inhibiting hypoxia (FIH) are reduced, favoring hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-α accumulation and its translocation to the nucleus. In the cell nucleus, the HIF-α/HIF-β heterodimer is formed. This forms a complex that binds to the hypoxia response elements (HRE) of HIF target genes and activates the expression of more than 200 genes, initiating the activation of cellular pathways to enhance the oxygen in the cells.