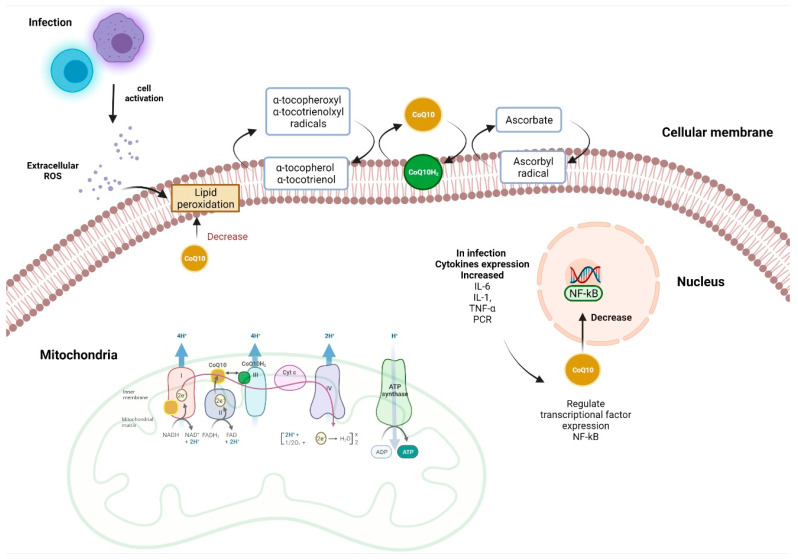
Figure 1.
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions of CoQ10. During an infectious process, the cells of the immune response produce cytokines and reactive oxygen species (ROS) as a mechanism to combat a pathogen, these ROS can produce lipoperoxidation, which can be inhibited by the direct antioxidant effect of CoQ10. The main function of CoQ10 in the mitochondria is to transfer electrons to complex III (CIII). By transferring two electrons to Complex III, the reduced form of CoQ10 (ubiquinol) is oxidized to ubiquinone. The ubiquinol pool can be restored by accepting electrons from members of the electron transport chain (CI and CII). The anti-inflammatory effects of CoQ10 may be linked to the regulation of IL-1, IL-6, CRP and TNF-α gene expression through the NF-kB pathway. Figure was created with BioRender software, (Toronto, ON, Canada) ©biorender.com.