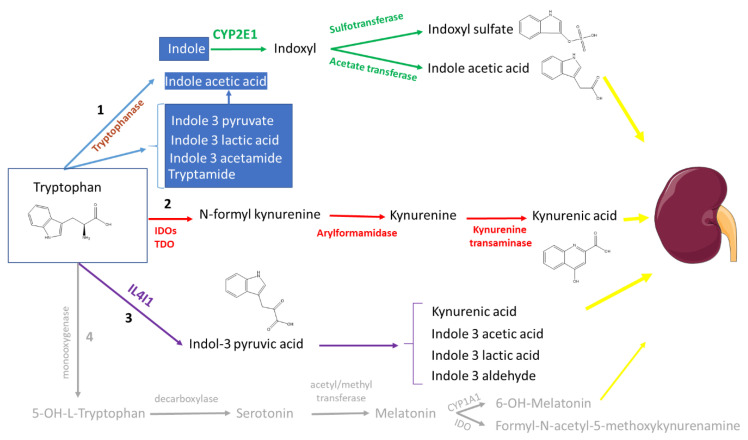
Figure 1.
Global metabolic pathways of tryptophan according to the most recent insights. Different enzymes are involved in the generation of uremic toxins and activators of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). (1) Tryptophanase; (2) indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenases (IDOs) and tryptophan-2,3-dioxgenase (TDO) and (3) the newly identified interleukin 4-induced-1 (IL4I1). Indole is further metabolized in the liver (green arrows) by cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily E member 1 (CYP2E1), resulting in indoxyl and indoxyl sulfate (sulfotransferase) and indole-3-acetic acid (acetate transferase). Both the IDOs/TDO (red arrows) and IL4I1-dependent pathways (purple arrows) are involved in the generation of kynurenic acid. The end-metabolites are excreted by the kidneys (yellow arrows). For the sake of completeness, in grey, (4) the serotonin pathway.