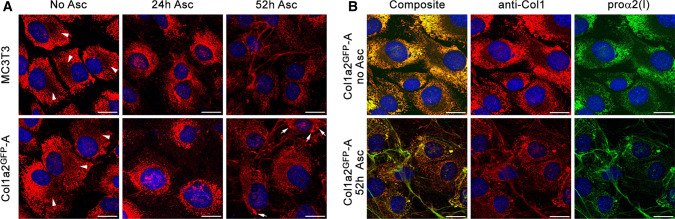
Fig. 2.
Procollagen, collagen, and GFP-proα2(I) localization in Col1a2GFP cells and extracellular matrix. a Immunofluorescence of procollagen and collagen molecules in fixed MC3T3 and Col1a2GFP-A cells imaged with collagen triple helix antibody (anti-Col1) before and after treatment with ascorbic acid 2-phopsphate (Asc2P). Bright ER labeling combined with distinct perinuclear shadows (arrowheads) indicates procollagen retention in the ER and empty Golgi before Asc2P addition. Most procollagen is translocated from the ER to Golgi 24 h after Asc2P addition. Normal steady-state procollagen trafficking and collagen fiber formation is observed 52 h after initial addition of Asc2P. Arrows show procollagen pools likely within dilated ER regions (see Fig. 7). b Colocalization of anti-Col1 with GFP-proα2(I) inside Col1a2GFP-A cells and in extracellular fibers. Complete colocalization indicates efficient incorporation of GFP-proα2(I) chains followed by folding and secretion of the resulting procollagen molecules. Less efficient staining of extracellular fibers by anti-Col1 relative to GFP-proα2(I) is likely related to reduced binding of this antibody to collagen triple helices at fiber surfaces. Scale bars = 20 µm