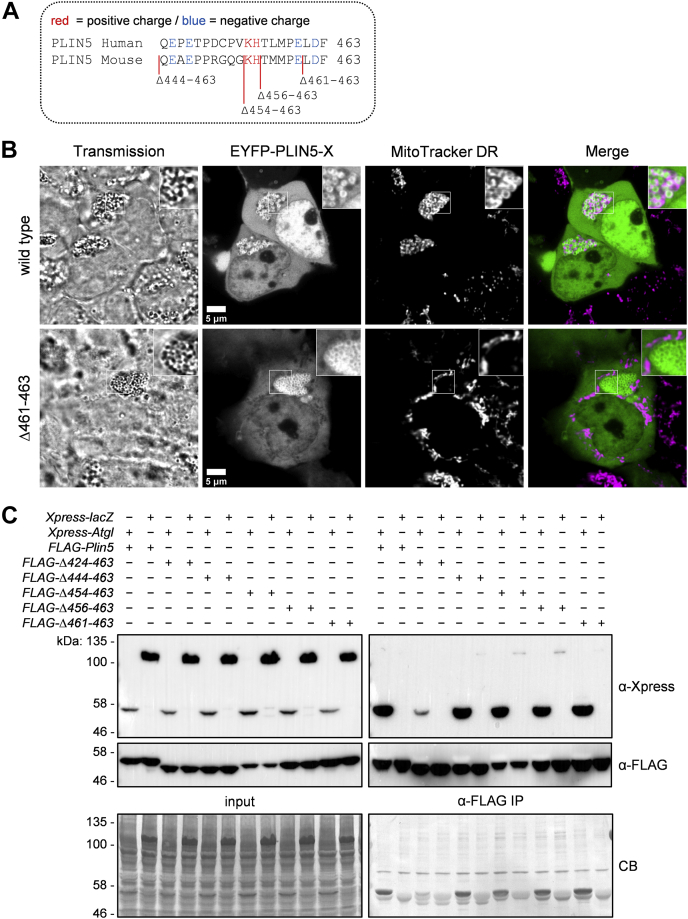
Fig. 2.
Generation of truncated PLIN5 variants specifically lacking interaction with mitochondria, while maintaining normal interaction with ATGL. A: Protein sequence alignment of the conserved carboxyl terminus of human and murine PLIN5. Positive or negative charged polar amino acid residues are highlighted in red and blue, respectively. Vector constructs encoding C-terminally truncated PLIN5 mutants were generated by inserting stop codons into the Plin5 CDS via site-directed mutagenesis. B: Truncation of the C-terminal Leu-Asp-Phe (LDF) sequence of PLIN5 is sufficient to disrupt LDMC. Human embryonic kidney-293T (HEK-293T) cells transiently expressing EYFP-tagged wild type or mutant PLIN5 were cultured in medium containing oleic acid to promote LD formation. Mitochondria were stained using MitoTracker DR, and cells were analyzed by confocal microscopy. C: The region spanning amino acids 424–443 of murine PLIN5 is critical for robust protein interaction with ATGL. HEK-293T cells were cotransfected with plasmid DNA encoding recombinant proteins as indicated. Target proteins were detected in cell homogenates (input) and anti-FLAG IPs by immunoblot analyses using adequate antibodies. Coomassie blue (CB) staining confirmed equal protein loading. Insets, 2× magnification.