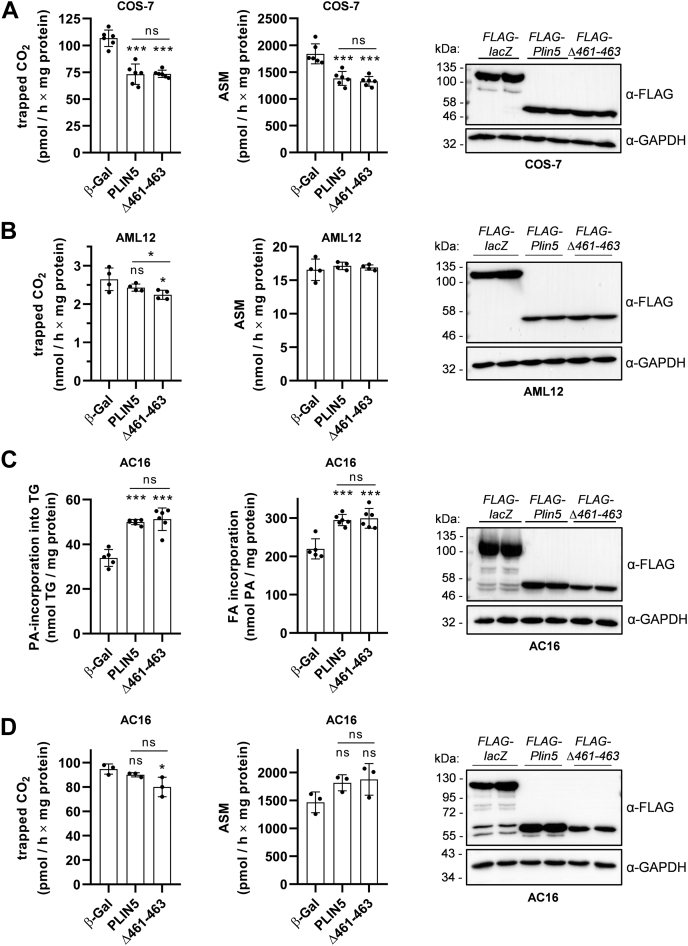
Fig. 6.
Disruption of LDMC has no major impact on β-oxidation rates of exogenously added or LD-derived FAs compared with cells with PLIN5-mediated LDMC. A, B: Acute β-oxidation rates of exogenously added PA-BSA of (A) COS-7 cells or (B) AML12 cells stably expressing recombinant target proteins as indicated. A, B, left panels: Released radiolabeled 14C-CO2 was trapped in NaOH-soaked filter paper and quantified by liquid scintillation counting. A, B, middle panels: The generation of PA-derived 14C-labeled ASMs was quantified by determining the radioactivity in culture medium supernatants. A, B, right panels: Immunoblot analyses verified similar expression levels of target proteins during the assays. C: Transgenic AC16 cells were pulsed with a mixture of 0.2 mM OA-BSA and 0.2 mM PA-BSA for 16 h, using 14C-labeled PA-BSA as tracer. PA-incorporation into TG (C, left panel) and total cellular PA uptake during the pulse (C, middle panel) were quantified by scintillation counting of TG fractions and culture medium supernatants, respectively. D: Oxidation rates of LD-derived FAs. Transgenic AC16 cells were pulsed as in (C), followed by stimulation of lipolysis via serum starvation and forskolin treatment. Released 14C-CO2 (D, left panel) and generated PA-derived ASM (D, middle panel) were quantified as mentioned. C, D, right panels: Overexpression of target proteins during the experiments was confirmed by immunoblot analyses. All data are presented as mean ± SD (A: n = 6; B: n = 4; C: n = 5–6; and D: n = 3). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student’s t-test (ns = not significant, ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. β-Gal).