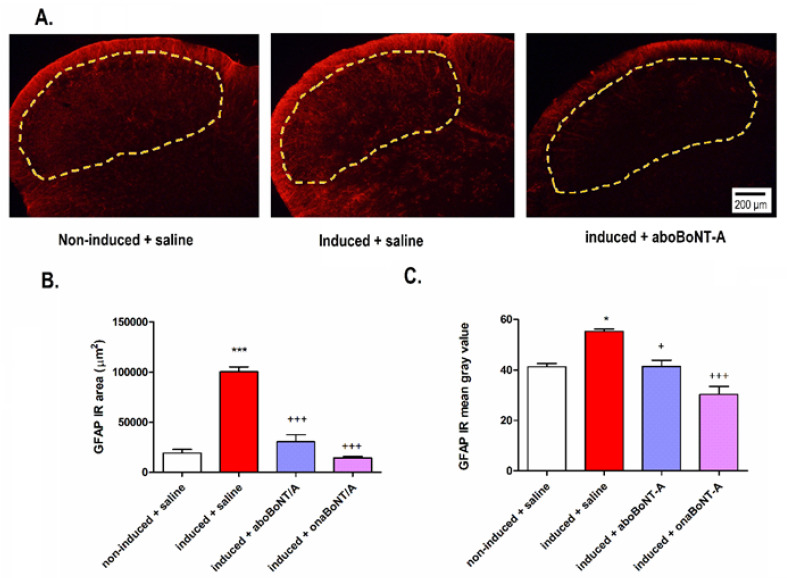
Figure 5.
Effects of abobotulinumtoxinA (aboBoNT-A, 15 U/kg) and onabotulinumtoxinA (onaBoNT-A, 7 U/kg) on glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) expression in the trigeminal nucleus caudalis (TNC) of rats exposed to the persistent immunogenic hypersensitivity model in the temporomandibular joint. (A) The representative microphotographs of TNC immunostained for GFAP (representative of 5 animals per group). Astrocyte activation was evident as (B) an increase in the GFAP-immunoreactive (IR) area and (C) increase in the mean intensity (mean gray value) of arthritis-induced animals and prevented by aboBoNT-A and onaBoNT-A. The analysis was performed on 5 randomly selected slices per animal (n = 5 animals/group). The yellow dotted lines indicate the analyzed TNC area. Mean ± SE; *** p < 0.001 and * = p < 0.05 vs. noninduced + saline and +++ = p < 0.001 and + = p < 0.05 vs. induced + saline (F3,16 (GFAP area) = 73.14; F3,16 (GFAP gray value) = 23.21; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test).