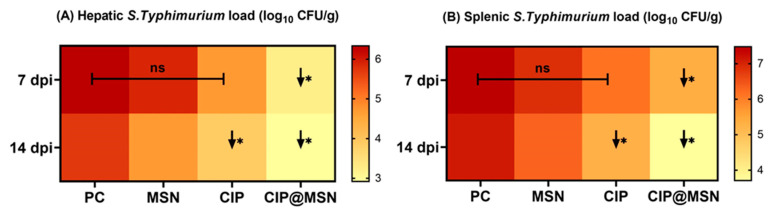
Figure 3.
In vivo evaluation of CIP–MSN treatment on S. typhimurium bacterial load in (A) hepatic tissue and (B) splenic tissue at 7and 14 days post-infection (7 and 14 dpi) by real-time PCR quantification of DNA copies, and represented as log10 of the CFU per gram of tissue. PC (positive control): rats received a control diet without any addition and were orally challenged with S. typhimurium; MSN(mesoporous silica particles): rats received a control diet, were orally challenged with S. typhimurium, and received 10 mg/kg MSN orally twice a day for 3 days; CIP(ciprofloxacin): rats received a control diet, were orally challenged with S. typhimurium, and received 10 mg/kg CIP orally twice a day for 3 days; and CIP–MSN (MSN particles loaded with ciprofloxacin): rats received a control diet, were orally challenged with S. typhimurium, and received 5 mg/kg CIP orally twice a day for 3 days. Data are expressed as means ± SE (error bars). Arrows correspond to significant decrease (↓*) relative to the PC group (p < 0.05), and NS represents nonsignificant differences relative to the PC group (p-value > 0.05).