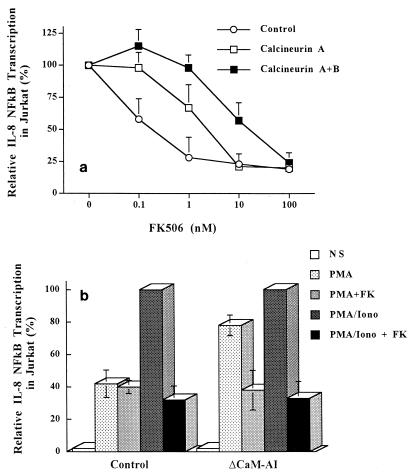
FIG. 4.
Involvement of calcineurin in transcriptional activation of IL-8 NF-κB. (a) Attenuation of IL-8 NF-κB sensitivity to FK506 inhibition by calcineurin expression in plain Jurkat T cells. All transfections include the IL-8 NF-κB luciferase reporter plasmid and either the pEF/CaA-expressing catalytic subunit of calcineurin (closed squares), the pEF/CaA- plus pEF/CaB-expressing regulatory subunits of calcineurin (open squares), or mock plasmid pEF(−) (open circles). At 15 h following transient cotransfection, the cells which had already been treated for 1 h with FK506 were stimulated with PMA (20 ng/ml) plus ionomycin (2 μM) (PMA/Iono) for 4 h in the presence of the drug. (b) Upregulation of transcriptional activation of IL-8 NF-κB by constitutively active calcineurin in an FK506-sensitive manner. Plain Jurkat T cells were transiently cotransfected with reporter plasmid pκB-8/luc and either a control expression vector, pEF(−) (Control) or pEF/ΔCaM-AI, that constitutively expresses the catalytic subunit of calcineurin (ΔCaM-AI). Following 15 h of recovery, the cells were pretreated with FK506 and were then stimulated as described above for panel a. Whole-cell extracts were prepared, and luciferase assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods. NS, nonstimulated; FK, FK506. In each experiment, the luciferase activity produced was normalized to the amount of β-galactosidase activity and protein concentrations. Data represent means ± standard deviations for three independent experiments.