Figure 1.
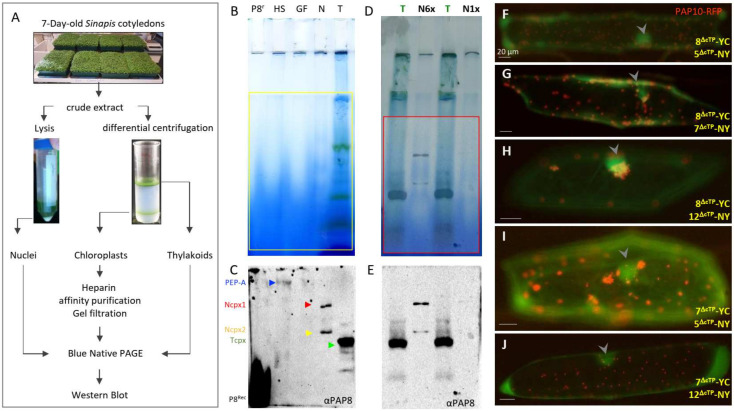
PAP8 is detected within a nuclear subcomplex. (A) Organelle fractionation, purification scheme, and sample processing. BN-PAGE, blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. (B,D) BN-PAGE and corresponding Western blot analyses in (C,E) using the PAP8 antibody. P8r, recombinant PAP8 protein purified from E. coli; HS heparin Sepharose fraction produced with the intact chloroplast sample; GF, gel filtration sample following HS; N, N6×, and N1× different loading of the sonicated and soluble nuclear fraction (see Section 4). T, thylakoid fraction from broken CP. (C) arrowheads, blue for PEP-A, red for the Ncpx1 (large nuclear complex), yellow Ncpx2 (smaller complex), green for the thylakoid PAP8-containing complex, and αPAP8 for the primary anti-PAP8 antibody. (F–J) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation tests using in combination PAP8ΔcTP-YC (8ΔcTP-YC) with PAP5ΔcTP-NY (5ΔcTP-NY) in (F); 8ΔcTP-YC with PAP7ΔcTP-NY (7ΔcTP-NY) in (G); 8ΔcTP-YC with PAP12ΔcTP-NY (12ΔcTP-NY) in (H); 7ΔcTP-YC 5ΔcTP-NY) in (I) and 7ΔcTP-YC with (12ΔcTP-NY) in (J); PAP10-RFP was used as internal positive control for transfection. Arrowheads indicate nuclei. Transgenes expressed under CaMV35S promoter (see [27] for published control experiments). Scale bars equal 20 µm.