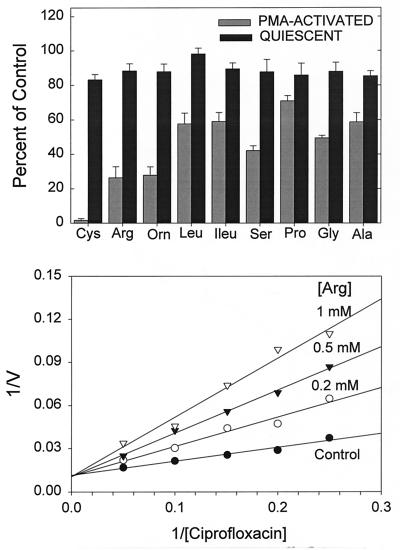
FIG. 3.
Inhibition of ciprofloxacin transport by l-amino acids. (Upper panel) Quiescent and PMA-activated neutrophils were incubated with ciprofloxacin at 5 μg/ml and the indicated amino acids at 1 mM, and transport was monitored for 5 min. Results are expressed as the means ± standard errors of the means for three experiments. In PMA-activated cells, the amino acids produced a significant treatment effect (P < 0.001, repeated-measures ANOVA), and each amino acid produced significant inhibition relative to controls (P < 0.05, Dunnett’s test). In quiescent cells, the treatment effect was not statistically significant (P = 0.17, repeated-measures ANOVA). (Lower panel) Competitive inhibition of ciprofloxacin uptake by arginine in PMA-activated neutrophils. The figure was derived from one of four replicate experiments. The observed Ki for arginine was 175 ± 25.4 μM. V, velocity.