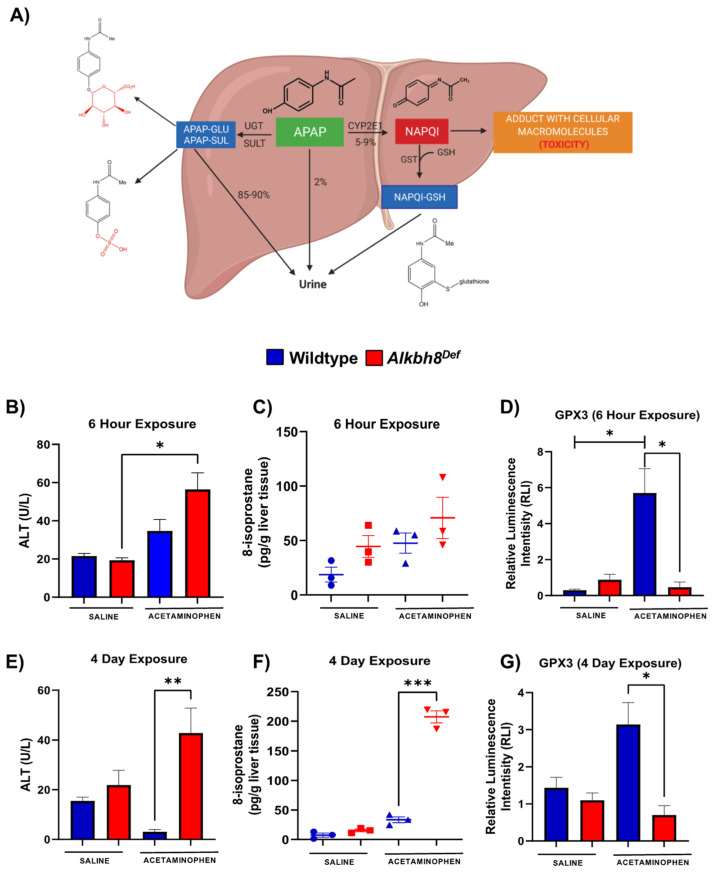
Figure 1.
Writer deficient mouse livers have increased sensitivity to APAP induced stress and display decreased selenoprotein levels. (A) APAP can be converted into a non-toxic form by UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGT) or a toxic form by cytochrome P450 enzyme (CYP2E1) to generate the reactive intermediate metabolite N-actyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI). Male C57Bl/6 WT (blue) and Alkbh8Def (red) mice (8–12 weeks old) were exposed to a single dose of APAP (B–D) or daily dose of APAP over 4 days (E–G), and tissue/blood was harvested. (B,E) ALT and (C,F) 8-isoprostane levels were determined in blood and liver samples, respectively for WT saline (blue circle), Alkbh8Def saline (red square), WT APAP (blue triangle) and Alkbh8Def APAP (red triangle) (D,G) Gpx3 protein levels in the liver were evaluated using the ProteinSimple WES system. Statistical significance (N = 3) was measured by an unpaired t-test with (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001).