Figure 1.
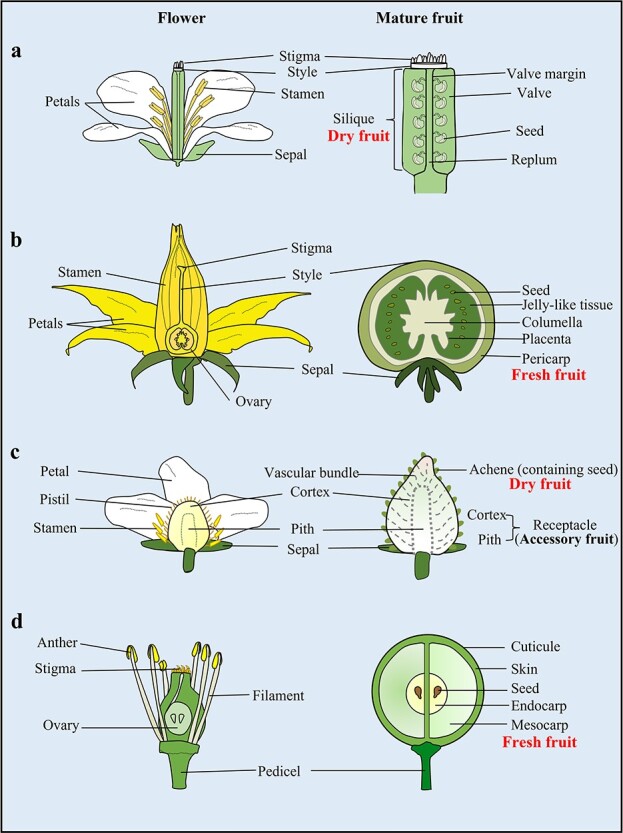
Schematic representation of longitudinal sections of flowers and fruits. a The Arabidopsis fruit is a silique formed from fused carpels. After fruit maturation, the valve margins differentiate into a dehiscence zone for fruit opening [13, 14]. b The tomato fruit is a fleshy fruit, a syncarpous gynoecium of several fused carpels with many seeds embedded in a fleshy mass [14–16]. c Strawberry has many individual pistils in a single flower, and the fleshy part of the strawberry is the receptacle (accessory fruit, which is the tip of the stem). The true fruit of the strawberry is a dry indehiscent fruit, the achene (the true fruit, which contains the seed) on the surface of the receptacle [17]. d The grape berry is a fleshy fruit, a syncarpous gynoecium of fused carpels. The ovary wall becomes the pericarp, which is composed of the skin, mesocarp, and endocarp [18].
