Figure 1.
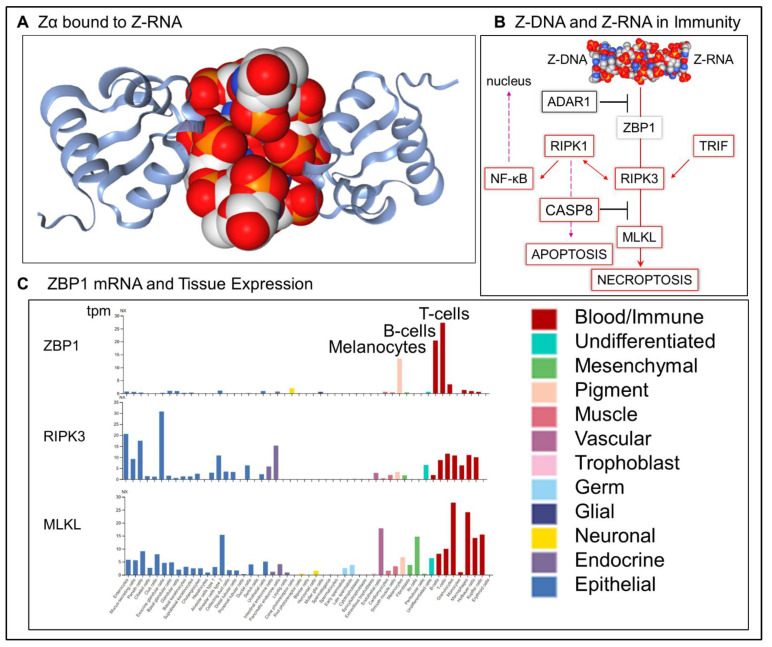
Z-DNA binding protein 1 (ZBP1) has different roles in development of the immune system. (A). Structure of the Z-DNA binding protein Zα2 domain bound to the zig-zag backbone of left-handed Z-RNA (from PDB:3EY1 rendered by NGL Viewer [22]). (B) ZBP1 senses left-handed Z-DNA and Z-RNA to initiate cell death, either by apoptosis or necroptosis. Both pathways depend on an interaction of receptor interaction protein kinase I and RIPK3. RIPK3 can also be activated by TRIF (toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 1 encoded by TICAM1). Execution of apoptosis depends on caspase 8 activation (CASP8), a protein that also inhibits RIPK3 activation of MLKL( mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase). ADAR1 (adenosine deaminase RNA specific) inhibits activation of ZBP1 through its Zα domain). RIPK1 is also able to activate the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) that then translocates to the nucleus. (C) Expression of ZBP1 in normal tissues is highest in T cells, B cells and melanocytes as measured by tpm (transcripts per kilobase million).