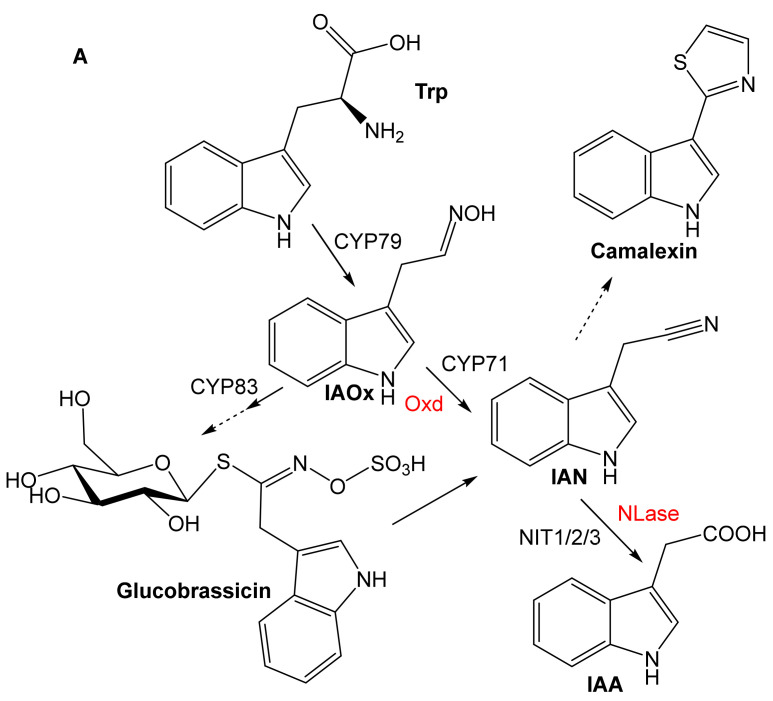
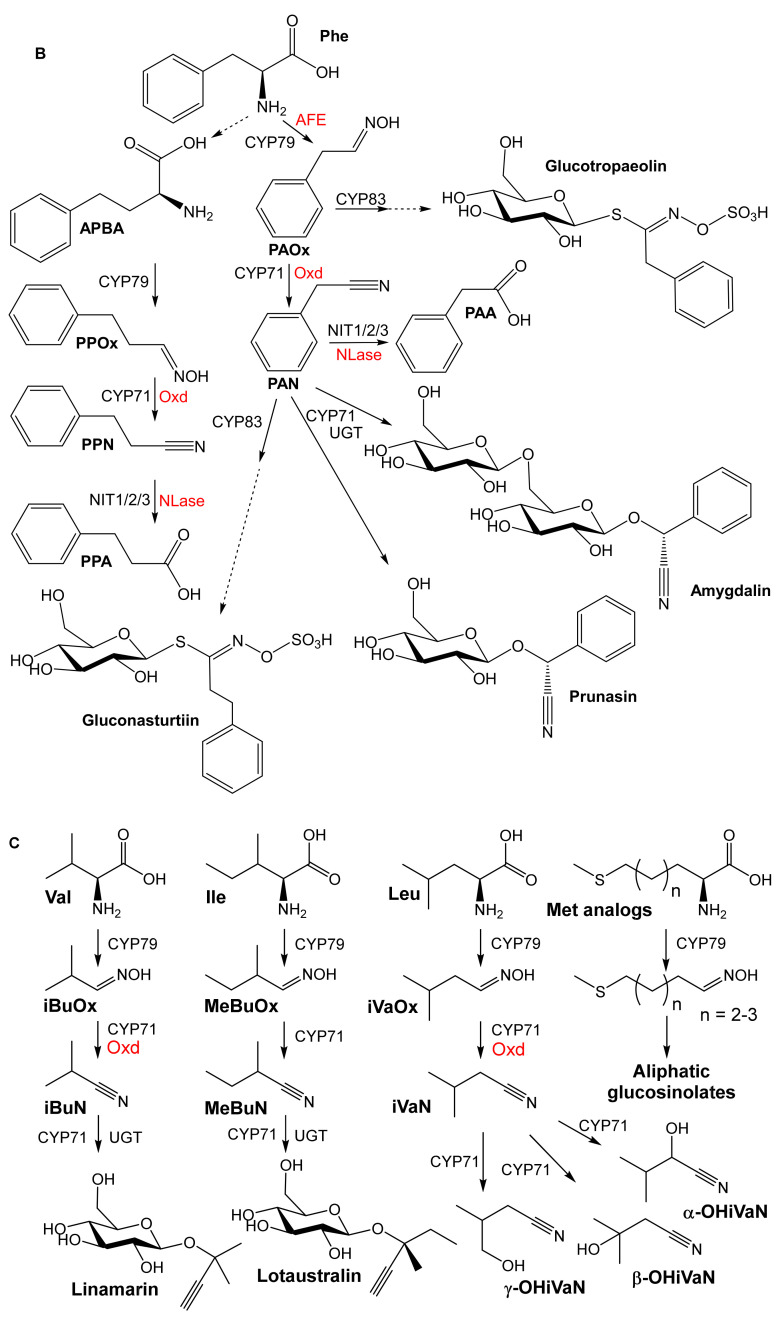
Figure 3.
Plant and bacterial metabolism of (A) indole-3-acetaldoxime (IAOx), (B) phenylacetaldoxime (PAOx), 3-phenylpropionaldoxime (PPOx), (C) isobutyraldoxime (iBuOx), 2-methylbutyraldoxime (MeBuOx), isovaleraldoxime (3-methylbutyraldoxime; iVaOx), and methionine analogs (according to [1,3,27], modified). Plant and bacterial enzymes are shown in black and red, respectively. The hydroxy derivatives of iVaN are transformed to various glucosides (not shown). AFE, aldoxime-forming enzymes; APBA, 2-amino-4-phenylbutyric acid; CYP, cytochrome P450 (CYP71, CYP79, and CYP83 family); IAN, indole-3-acetonitrile; IAA, indole-3-acetic acid; iBuN, isobutyronitrile; iVaN, isovaleronitrile; MeBuN, 2-methylbutyronitrile; NIT1/2/3, plant nitrilases of NIT1, NIT2, and NIT3 type; NLase, nitrilase; PAA, phenylacetic acid; PAN, phenylacetonitrile; PPA, 3-phenylpropionic acid; PPN, 3-phenylpropionitrile; UGT, UDP-glucosyl transferase.