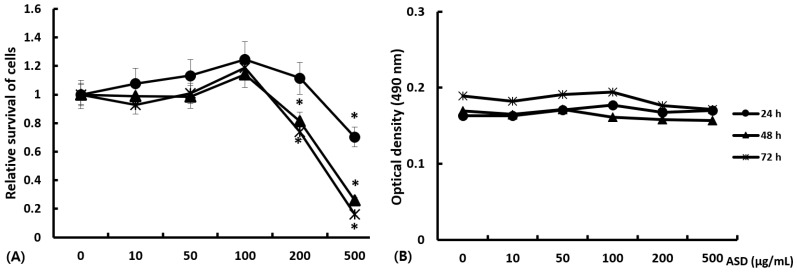
Figure 1.
Cell viability effect of Asian sand dust (ASD) on primary nasal epithelial cells. (A) shows relative survival of nasal epithelial cells treated with 0 to 500 μg/mL of ASD for 72 h. Cell survival was significantly decreased above ASD concentrations of 200 μg/mL. Stimulation time did not influence the survival of nasal epithelial cells. (B) shows absolute optical density of different ASD concentrations without cells. *: p < 0.05 compared to without ASD, k = 10.