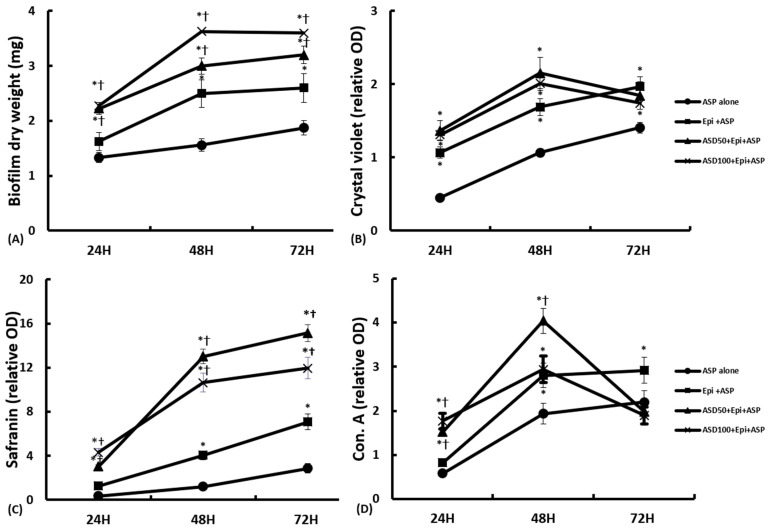
Figure 3.
Quantification of Aspergillus fumigatus (ASP) biofilm in coculture of Asian sand dust (ASD) in primary nasal epithelial cells. The biofilm dry weight (A) and safranin staining (C) intensity significantly increased in a time-dependent manner, and the ASP and ASD coculture in nasal epithelial cells (ASD+Epi+ASP) significantly increased the biofilm dry weight and safranin intensity compared to ASP cultured with nasal epithelial cells (Epi+ASP) or without nasal epithelial cells (ASP alone). When the ASP was cocultured with 50 μg/mL of ASD (ASD50) or 100 μg/mL of ASD (ASD100), the crystal violet (B) and concanavalin A (Con. A) staining (D) intensities were increased at 24 h and 48 h of incubation. However, their staining intensities were decreased at 72 h. *: p < 0.05 compared to ASP alone, †: p < 0.05 compared to Epi+ASP, k = 14.