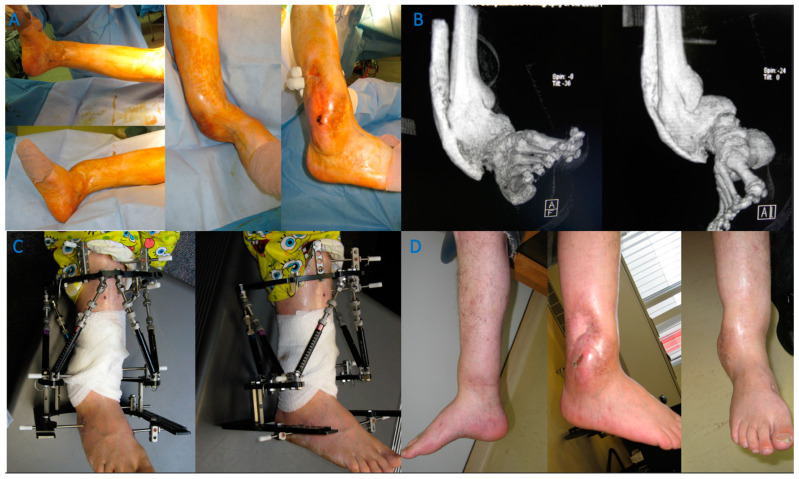
Figure 5.
A case of a severe distal tibia deformity with obvious soft tissue damage on the lateral border of the deformity. Conventional X-rays were unable to fully assess or define the deformity that can be seen on a 3D reconstruction CT scan (B). Image (A) depicts a gross image. An osteotomy and fixation with a Tayler Spatial Frame (C) were used with a residual calculation to slowly correct the deformity. Slow correction would help protect the soft tissue envelope on the lateral border and stretch the medial soft tissues. Correction has resulted in a plantigrade foot with motion of the ankle and a healed tibia (D).