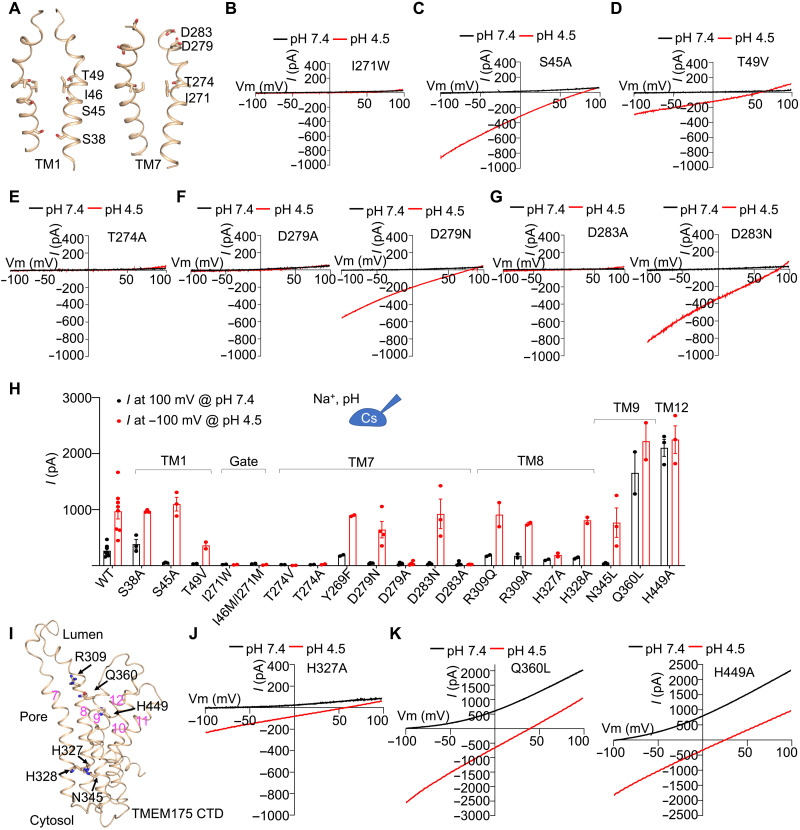
Fig. 7. Residues critical for potassium ion and proton permeation.
(A) Pore-lining residues in hsTMEM175 that we tested in this study for functional involvement in proton and K+ conductance. (B) Representative I-V curves of hsTMEM175 mutant I271W at pH 7.4 and pH 4.5, showing the abolishment of K+ and proton currents. (C) Representative I-V curves of hsTMEM175 mutants S45A at pH 7.4 and pH 4.5, showing abolished K+ conductance but normal proton conductance. (D) Representative I-V curves of hsTMEM175 mutants T49V at pH 7.4 and pH 4.5, showing abolished K+ conductance and reduced proton conductance. (E) Representative I-V curves of hsTMEM175 mutant T274A at pH 7.4 and pH 4.5, showing the abolishment of both proton and K+ currents. (F and G) Representative I-V curves of hsTMEM175 mutants D279A, D279N, D283A, and D283N at pH 7.4 and pH 4.5, showing their effects on K+ and proton conductance. (H) Averaged currents at 100 mV of pH 7.4 or −100 mV of pH 4.5 for hsTMEM175 WT and mutants. Data are presented as means ± SEM for n ≥ 3. (I) Residues on TM8, TM9, and TM12 that were examined for the regulation of proton conductance. (J) Representative I-V curves of hsTMEM175 mutant H327A, showing the deficiency in K+ and proton conductance. (K) Representative I-V curves of hsTMEM175 mutants Q360L and H449A, showing enhancement of K+ and proton conductance.