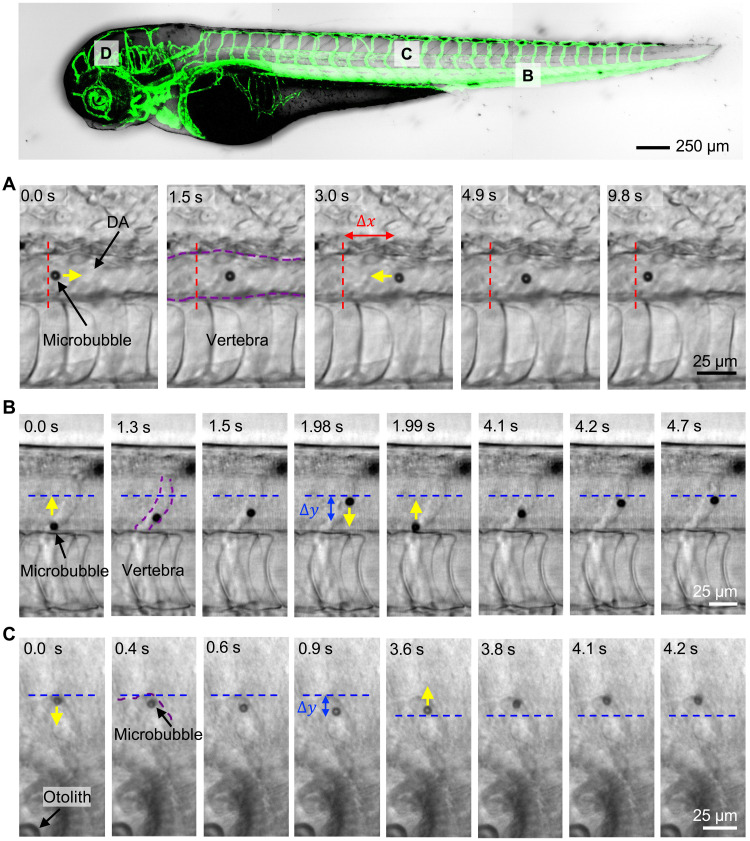
Fig. 4. Acoustic manipulation in vivo at different locations within the zebrafish vasculature.
To demonstrate full directional control, a bubble was directed along the vasculature and back to its initial position multiple times by shifting the frequency. (A) The microbubble was reversibly moved horizontally 22 μm left and right in the 21-μm-wide DA by varying the frequency controlling the horizontal position fx between 4.1 and 4.15 MHz at a constant amplitude of 10 VPP. (B) The bubble likewise traveled and returned 29.85 μm in the y direction without stiction in the ISV, which has a diameter close to that of contrast agents and passing RBCs by varying the frequency controlling the vertical position fy between 4.15 and 4.25 MHz at a constant amplitude of 12.5 VPP. (C) Last, the same reversible behavior was demonstrated with a traveled distance of 9 μm in a cerebral blood vessel, close to the otoliths by varying the frequency controlling the vertical position fy between 4.1 and 4.25 MHz at a constant amplitude of 10 VPP.