Figure 1.
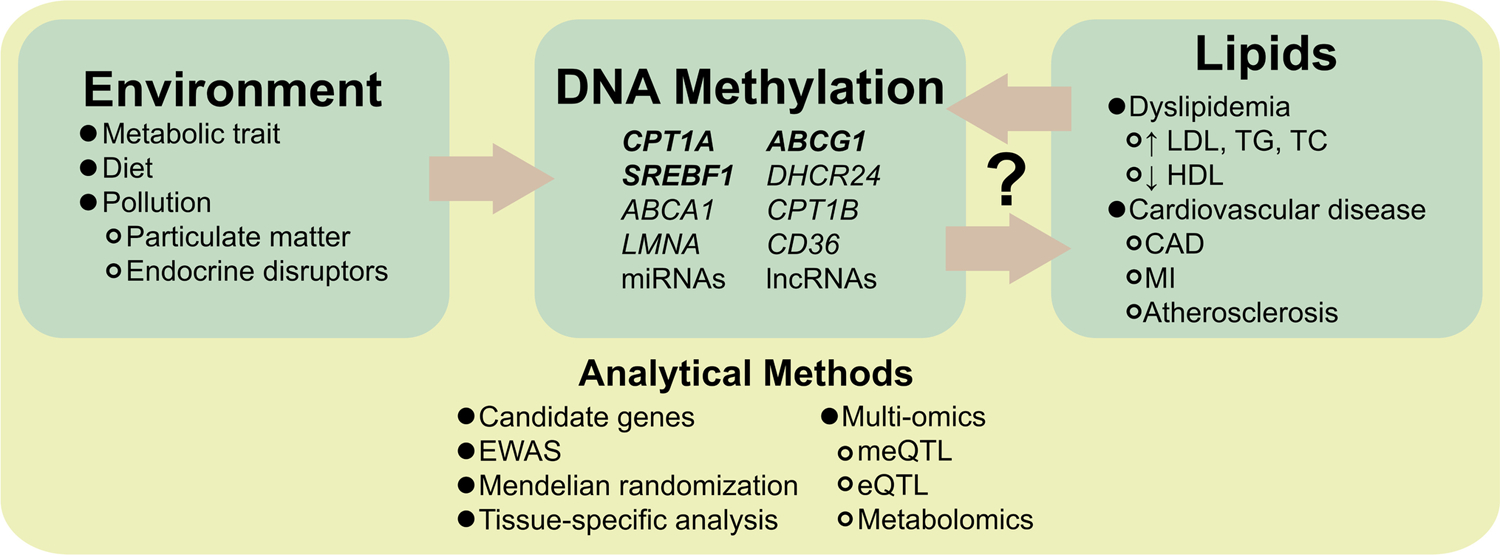
The interrelation of the environment, epigenome, and lipids are not fully understood. Environmental factors may induce methylation changes at genes that are associated with lipid traits. Conversely, Mendelian randomization studies suggest that lipid traits are causal for methylation. Further studies (via a diverse set of analytical methods) are needed clarify the directionality of these relationships. Abbreviations: microRNA (miRNA); long non-coding RNA (lncRNA); low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL); triglycerides (TG); total cholesterol (TC); high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL); coronary artery disease (CAD); myocardial infarction (MI); epigenome-wide association study (EWAS); methylation quantitative trait loci (meQTL); expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL).
