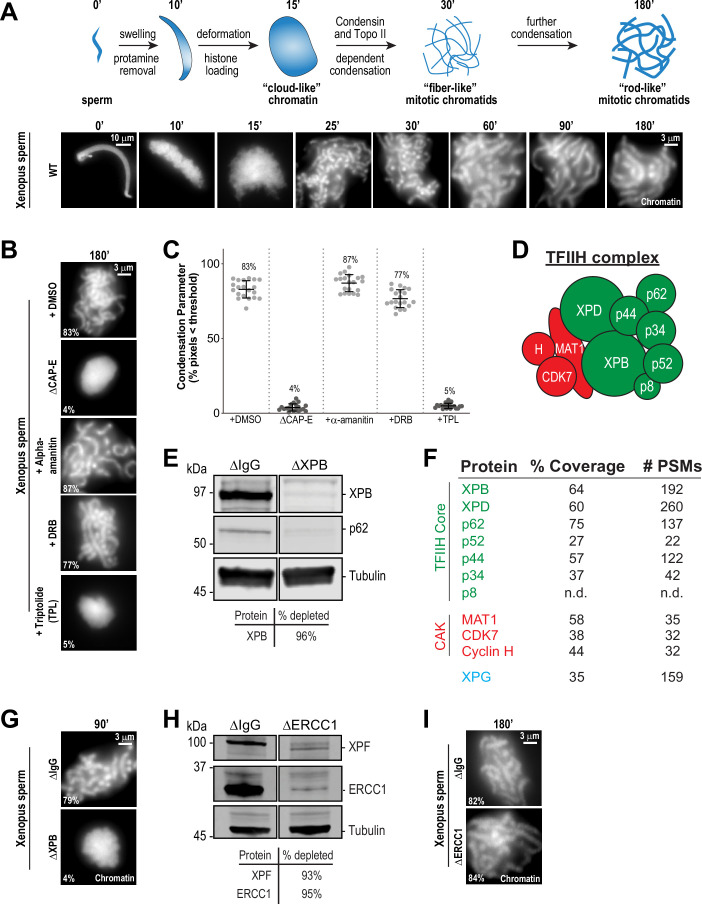
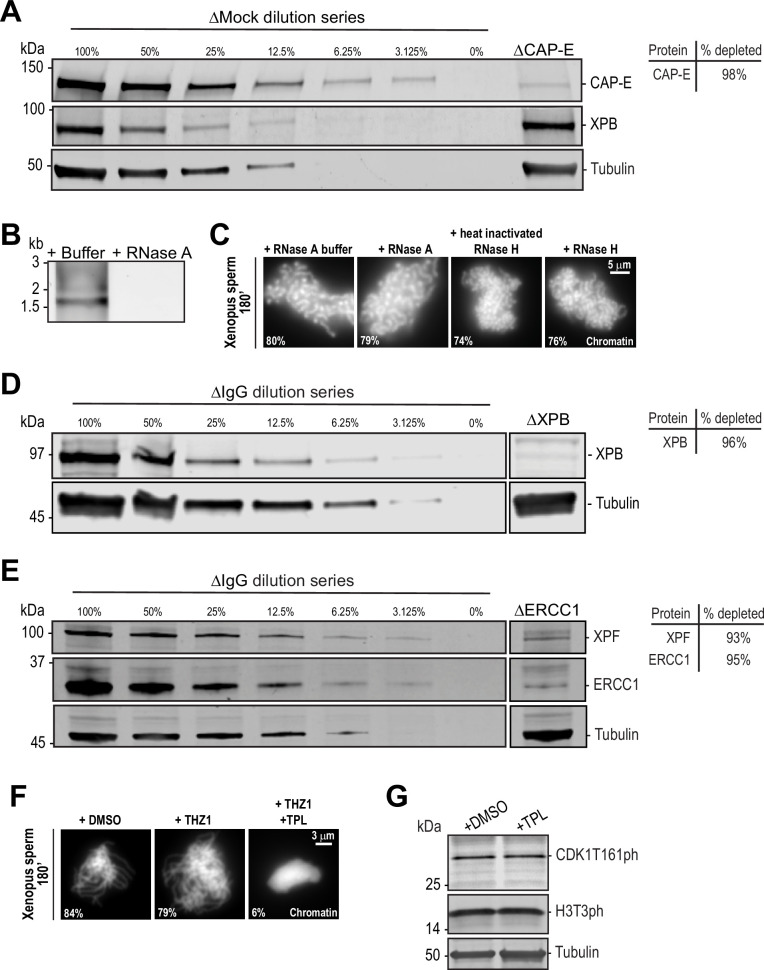
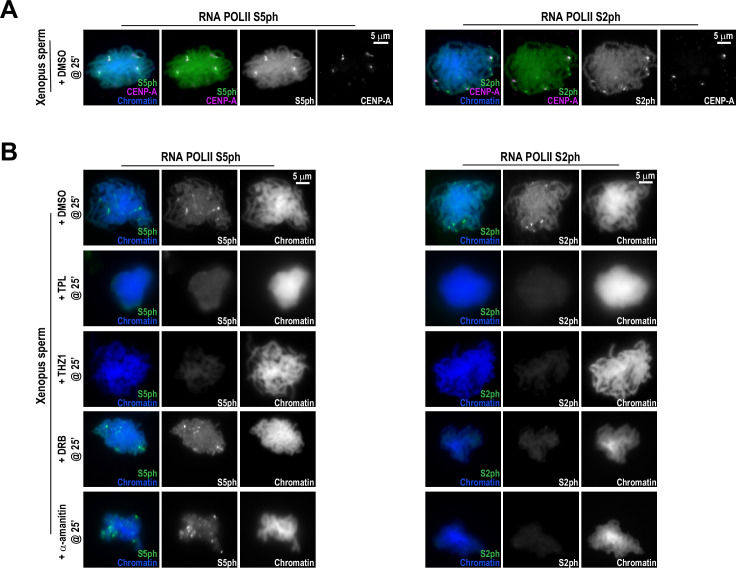
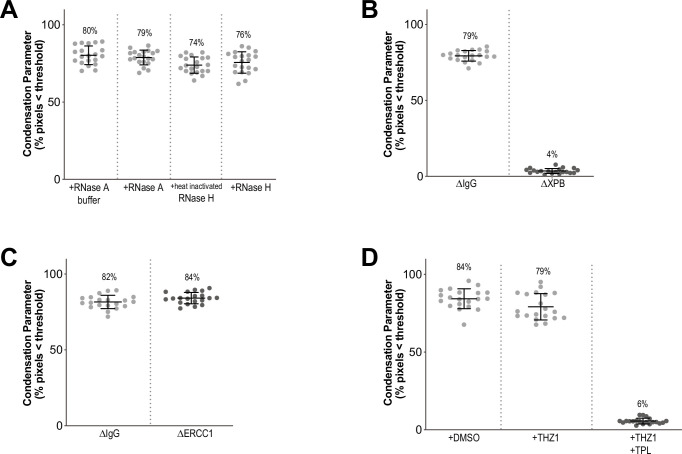
Figure 1. The TFIIH complex is required for chromosome condensation in Xenopus egg extracts.
(A) Top: Schematic of chromatid assembly in M-phase high-speed supernatant (HSS) extract. Bottom: Representative fluorescence images of fixed samples from a chromatid assembly reaction taken at indicated timepoints after sperm addition. Chromatin was stained with Hoechst. (B) Representative fluorescence images of chromatid assembly at steady state (180 min after sperm addition) in the presence of indicated inhibitors. Each drug or DMSO control was added at 25 min to exclude effects on the protamine-histone exchange process. Final inhibitor concentrations: Triptolide (50 μM), DRB (100 μM), and a-amanitin (54 μM). See Figure 1—figure supplement 1A for CAP-E depletion. Mean condensation parameters for each condition are indicated in lower left corner of each image. (C) Scatter plot of the percentage of pixels below a threshold of 35% of image maximum fluorescence intensity (the condensation parameter), which measures the progressive change in the fluorescence intensity distribution that occurs during condensation, for each condition. Error bars represent SD, and the mean values are indicated. n = 20 structures for each condition. Two biological replicates were performed, quantified structures are from a single experiment. (D) Schematic of the TFIIH complex. TFIIH core complex is green, CAK subcomplex in red. (E) Western blot for XPB, p62, and Tubulin in IgG or XPB-depleted extracts. (F) TFIIH complex members that interact with XPB in M-phase HSS extract, as identified by mass spectrometry. Purifications were performed in the absence of chromatin. PSMs = peptide spectrum matches. (G) Representative fluorescence images of chromatid assembly 90 min after sperm addition in IgG or XPB depleted extracts. Chromatin was stained with Hoechst. (H) Western blot for XPF, ERCC1, and Tubulin in IgG or ERCC1-depleted extracts. (I) Representative fluorescence images of chromatid assembly 180 min after sperm addition in IgG or ERCC1-depleted extracts. Chromatin was stained with Hoechst.