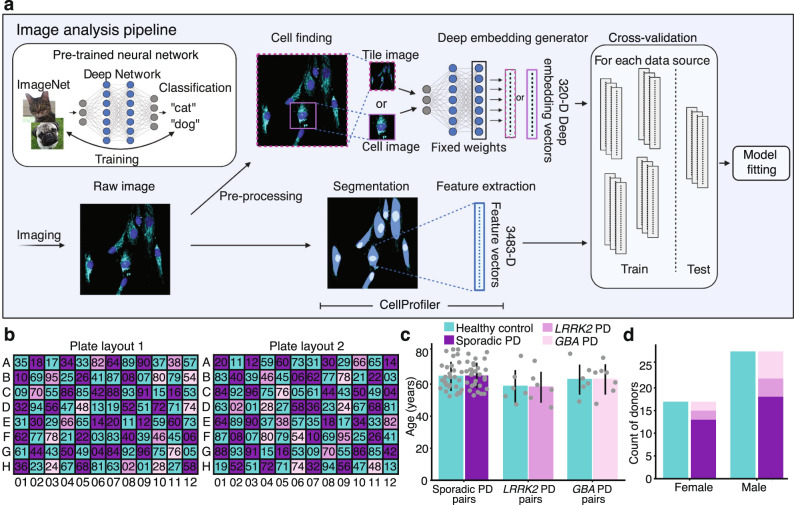
Fig. 2. Image analysis pipeline and rigorous experimental design enable unbiased deep learning–based high-content screening.
a A deep embedding generator (a neural network pre-trained on an independent object recognition task) maps each tile or cell image independently to a deep embedding vector, which along with CellProfiler features and basic image statistics were used as data sources for model fitting and evaluation for supervised learning prediction tasks including healthy vs. PD classification. b Two 96-well plate layouts used in each experimental batch control for location biases. In each layout, each well contained cells from one cell line denoted by the two-digit label. The second layout consisted of diagonally translating each of the four quadrants of the first. n = 45 healthy controls and n = 45 PD patients were matched in pairs based on demographics, including by c age and d sex. Data are presented as mean values ± standard deviation.