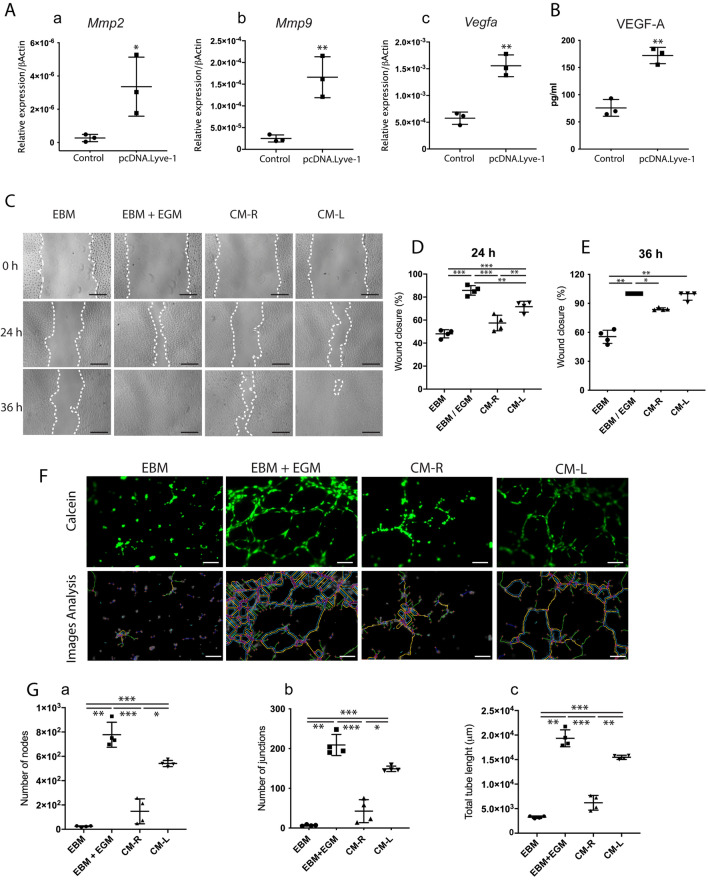
Figure 5.
LYVE-1-expressing macrophages promote the migration and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). A Lyve1-expression vector was transfected into RAW264.7 cells to generate Lyve1-expressing macrophages. (A) RT-PCR analysis of angiogenesis-related genes (Mmp2, Mmp9, and Vegfa) in RAW264.7 cells and Lyve1-expressing macrophages (mean ± SD, n = 3). (B) Quantification of VEGF-A in conditioned medium from Lyve1-expressing macrophages (CM-L) and RAW264.7 cells (CM-R) by ELISA (mean ± SD, n = 3). (C) Scratch wound healing test for HUVECs. The confluent cell monolayer of HUVECs was scratched with 200-μl pipette tips. Conditioned media (CM-L, CM-R), EBM-2 supplemented with EGM-2 (EBM/EGM), or serum-free EBM-2 (EBM) were added to culture plates. (D,E) Percentages of closure of scratched area at 24 h (mean ± SD, n = 4) and 36 h (median with interquartile range) after the initial scratch. Scratched areas were measured using an optimized plugin for ImageJ. (F) HUVEC tube formation assay. HUVECs were resuspended in conditioned media (CM-R, CM-L), EBM/EGM, or EBM. Cell suspension was seeded onto the solidified ECM gel and incubated for 6 h. Lower panels show the detection of tube-like structures of the corresponding upper panels using ImageJ. (G) The numbers of nodes and junctions and total tube length were quantified by ImageJ (mean ± SD, n = 4). Scale bars 300 µm (C) and 100 µm. Data were collected from 2–3 independent experiments to obtain consistent results. Data were statistically analyzed by unpaired Student’s t-test (Aa–c,B), one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test (D), Kruskal–Wallis test and Dunn's post hoc test (E), or Brown-Forsythe and Welch ANOVA test and Dunnett's T3 post hoc test (Ga–c). ∗p < 0.05, ∗ p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.0001.