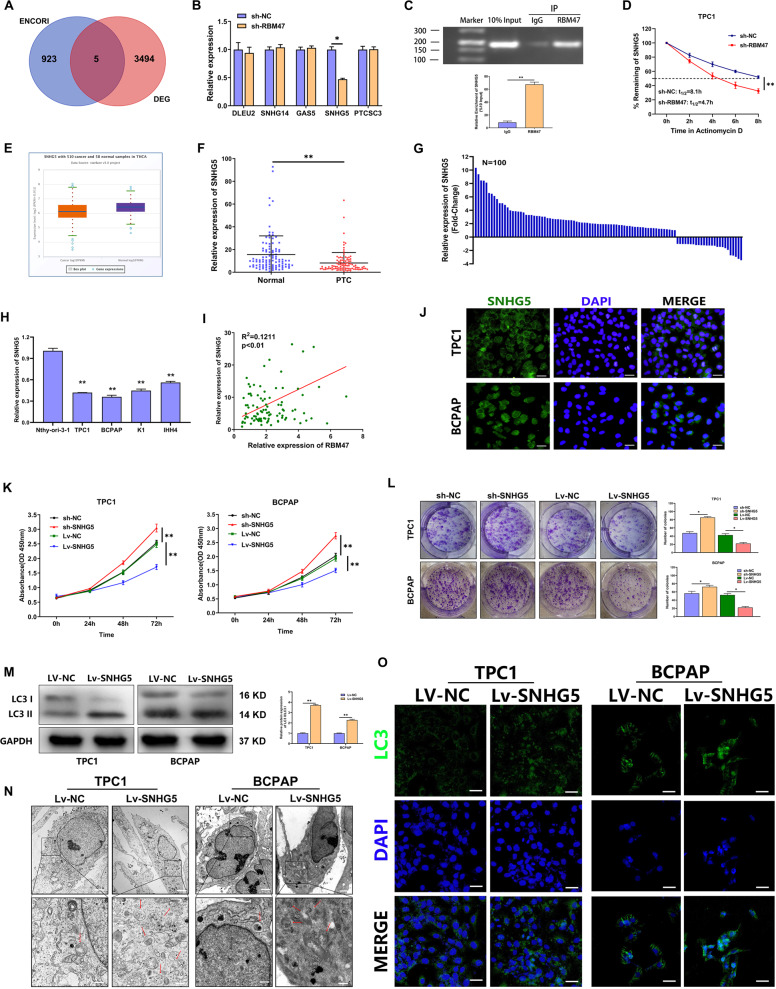
Fig. 3. RBM47 stabilized SNHG5 to inhibit proliferation and activate autophagy in PTC cells.
A The lncRNAs that potentially bind to RBM47 predicted by bioinformatics software. B The relative mRNA expression of related lncRNAs detected by qRT-PCR in TPC1 cells with RBM47 knockdown. C The enrichment of SNHG5 expression in anti-RBM47 precipitates shown by RIP assay. D The half-life of SNHG5 in TPC1 cells treated with RBM47 knockdown. E SNHG5 expression in PTC tissues and normal tissues from TCGA database. F The relative mRNA expression of SNHG5 in 100 paired PTC tissues and adjacent non-cancerous tissues. G The fold change of SNHG5 expression in 100 PTC tissues. H The relative mRNA expression of SNHG5 in PTC cells and normal thyroid cells measured by qRT-PCR. I The correlation between RBM47 and SNHG5 in PTC tissues. J The localization of GAS8-AS1 in cytoplasm verified by FISH. Scale bar = 20 μm. K, L Proliferation of SNHG5-silenced or -overexpressed cells evaluated by CCK-8 assay and plate colony assay. M–O LC3 II/LC3 I ratio detected by WB, LC3 puncta evaluated by IF and autophagosomes shown by TEM (red arrow) in PTC cells with SNHG5 upregulation. Scale bar in TEM = 5 μm (Upper) and 1 μm (Below), scale bar in IF = 20 μm. Statistical differences were analyzed using the independent samples t-test; data are shown as the mean ± standard error of the mean based on three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.