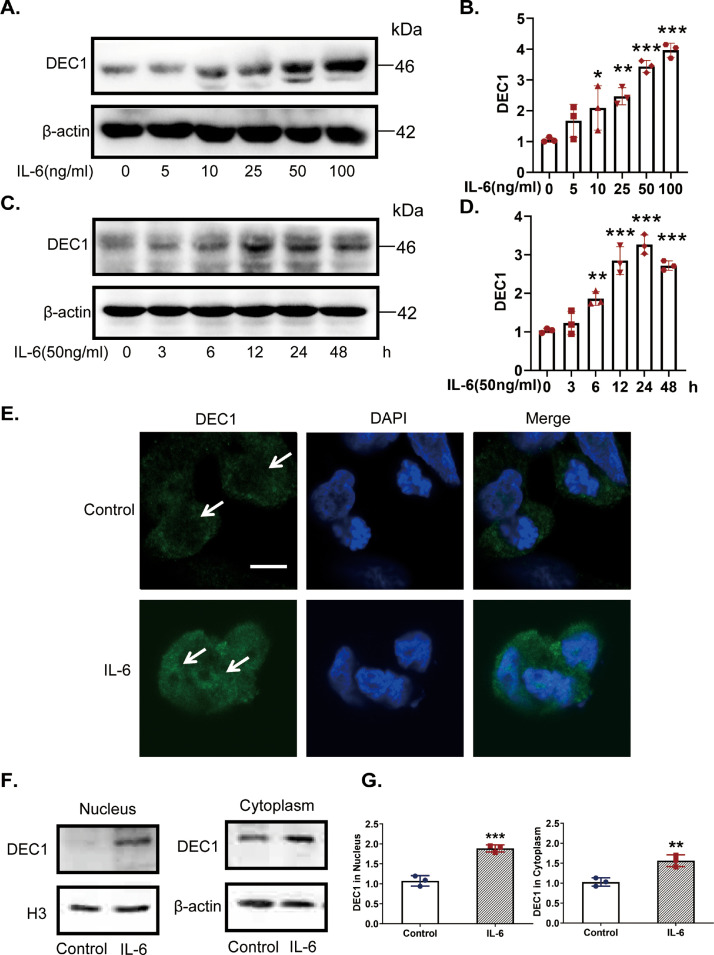
Fig. 5.
Increases of DEC1 expression and nuclear translocation in DLD-1 cells in response to IL-6. (A–D) IL-6 increases DEC1 expression, both in a dose- and time-dependent manner. DLD-1 cells were treated with IL-6 (0, 5, 10, 25, 50 and 100 ng/ml) for 24 h (one-way ANOVA, F (5, 12) = 21.87, p<0.0001. 0 vs. 10, p=0.0331, 0 vs. 25, p=0.0043, 0 vs. 50, p<0.0001, 0 vs. 100, p<0.0001), or were treated with IL-6 (50 ng/ml) for 0, 3, 6, 12, 24 or 48 h (one-way ANOVA, F (5, 12) = 45.57, p<0.0001. 0 vs. 6, p=0.0043, 0 vs. 12, p<0.0001, 0 vs. 50, p<0.0001, 0 vs. 100, p<0.0001). After that, the DEC1 expression was analyzed by Western blotting. (E) Effect of IL-6 on the DEC1 translocation with immunofluorescence analysis. DLD-1 cells were treated with IL-6 (50 ng/ml) for 24 h, and DEC1 protein translocation was monitored by immunofluorescence analysis. Scale bar=10 μm. (F, G) IL-6 induced DEC1 expression and translocation with plasmolysis. DLD-1 cells were treated with IL-6 for 24 h. DEC1 or β-actin cytoplasm protein (t-text, t=5.123, df=4, p=0.0069) and DEC1 or H3 nuclear protein expression (t-text, t=8.994, df=4, p=0.0008) were detected by Western blotingt. All experiments were repeated at least three times, and the data are expressed as mean ± SD. *p<0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. control or 0 h.