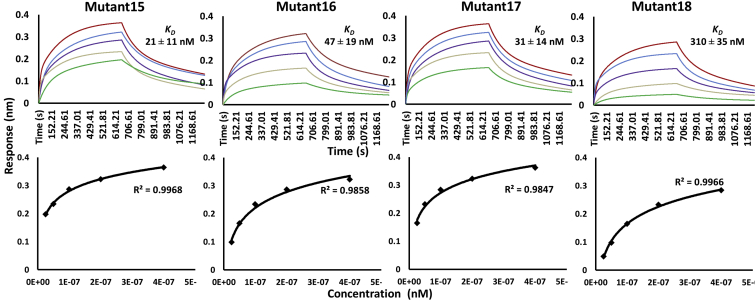
Figure 4.
Parallel sensor kinetics and equilibrium analyses of scFv triple mutant proteins’ binding to the Fu-bc subunit protein. The Fu-bc subunit protein was coupled to the BLI biosensor chip, and scFv triple mutants (Mutant14–18) were applied at graded concentrations (25–400 nM) over the coupled surface (from t = 0 to t = 660 s), followed by buffer washout (dissociation) for another 490 s and measurement of net binding (in RU). The association (ka) and dissociation rate constants (kd) were derived by fitting the recorded sensograms to a (1:1) kinetic titration series model, and the affinity constant KD was derived by dividing the dissociation constant (kd) with the association constant (ka). The overlay of curves for different concentrations of scFv protein was fitted into a numerical model by global analysis using BioEvaluation software 4.1. The color of each fitted curve shown is a representative response of different concentrations of analytes (i.e., green, 25 nM; golden, 50 nM; violet, 100 nM; blue, 200 nM; and red, 400 nM). Furthermore, the BLI responses at equilibrium were plotted against each of the injected protein concentrations (lower panel). The curves were fitted by nonlinear least squares regression. All the R2 values indicate that the regression model fits the data much better than the null hypothesis. Fu-bc, fusion and bc loop; scFv, single chain variable fragment antibody.