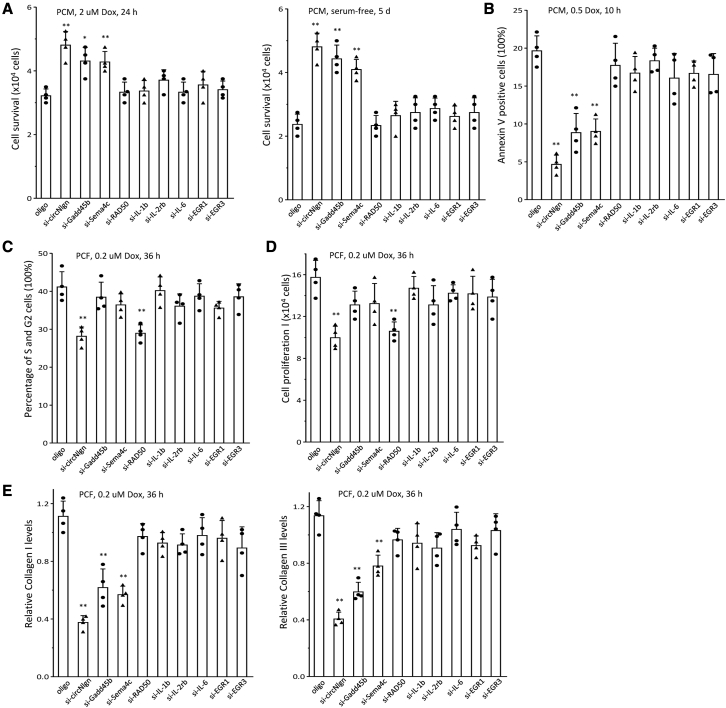
Figure 7.
Activation of H2AX by p38 and pJNK
(A) PCMs were transfected with siRNAs and cultured in basal medium with 2 μM doxorubicin for 24 h (left) or serum free for 5 days (right). Silencing circNlgn, Gadd45b, or Sema4C enhanced PCM survival. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 versus oligo (n = 4). (B) The transfected PCMs were cultured in basal medium with 0.5 μM doxorubicin for 24 h and subjected to Annexin staining followed by flow cytometry. Silencing circNlgn, Gadd45b, or Sema4C repressed PCM apoptosis. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus oligo (n = 4). (C) PCFs were cultured in basal medium treated with 0.2 μM doxorubicin for 36 h and then transfected with siRNAs. After 48 h, the cells were harvested and subjected to flow cytometry. Silencing circNlgn or RAD50 repressed PCF cycle entry. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus oligo (n = 4). (D) Cell proliferation assays showed that silencing circNlgn or RAD50 repressed PCF proliferation. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus oligo (n = 4). (E) PCR showed that circNlgn, Gadd45b, or Sema4C repressed collagen I (left) and collagen III (right) in the above doxorubicin-treated PCFs. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus oligo (n = 4). We found that transgenic expression of circNlgn mediates doxorubicin-induced cardiofibrosis. The protein Nlgn173 translated by circNlgn interacts and activates H2AX, resulting in upregulation of IL-1b, IL-2Rb, IL-6, EGR1, and EGR3. This mechanism may hold therapeutic implications for mitigating the side effects of doxorubicin in cancer treatment.