Figure 1:
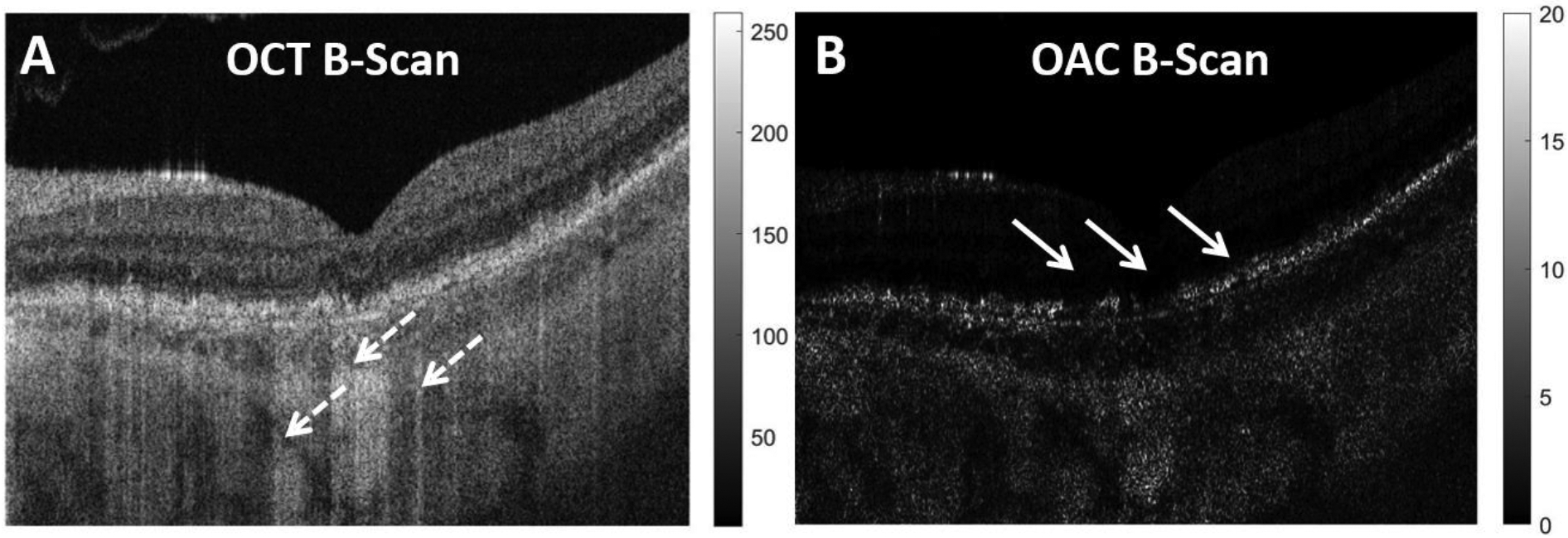
Example of a traditional swept source OCT (SS-OCT) B-scan and its corresponding optical attenuation coefficient (OAC) B-scan. A: SS-OCT B-scan from a patient diagnosed with geographic atrophy (GA), dashed white arrow indicates regions with choroidal hyper-transmission defects (hyperTDs) caused by compromised retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). B: Corresponding OAC B-scan of panel A, the solid white arrows indicate the areas where the RPE is compromised that’s responsible for the choroidal hyperTDs seen on the SS-OCT B-scan.
