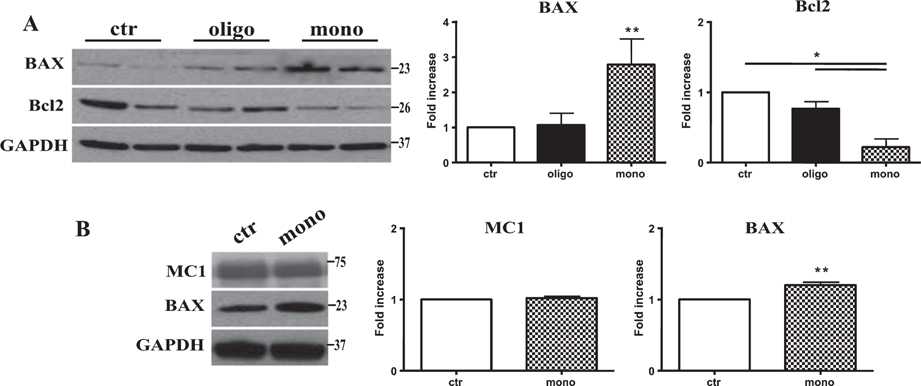
Fig. 5.
Tau monomers induce apoptotic cell death and maintain their toxicity also after 4 days treatment without affecting tau conformational changes. A) Representative western blotting of brain extracts from mice injected with control ACSF solution and tau peptides (ICV for 3 h) using BAX and Bcl2 antibodies for detection. Densitometric quantification shows that mTau causes a significant increase in proapoptotic protein BAX and a parallel decrease in the antiapoptotic protein Bcl2. By contrast, oTau caused only a significant increase in n Bax protein levels. B) Representative western blotting of brain extracts from mice injected with control ACSF solution and tau peptides (ICV for 4 days) using MC1 and BAX antibodies for detection. mTau does not modify the pathological conformation of Tau and maintains the ability to mediate apoptotic cell death. In all cases an antibody raised against GAPDH served as a loading control. The data are mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 versus control by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, n = 6.