FIGURE 3.
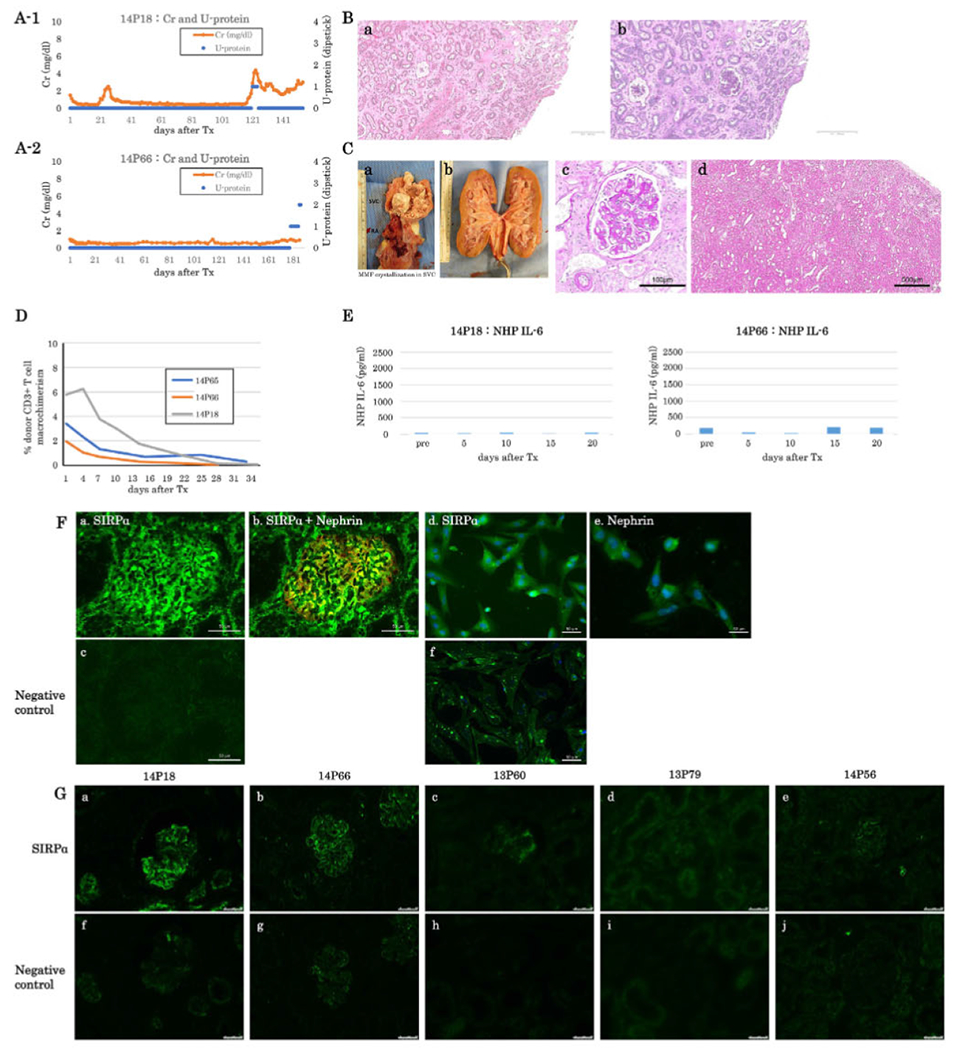
(A) sCre (orange lines) and urine protein (blue dots) of baboons following K+VT XTx in Group B with anti-IL6R Ab treatment (A-1: #14P18, A-2: #14P66). Both baboons survived over five months. Baboon #14P66 developed 2+ proteinuria only in the last two days (A-2). (B) Excised graft kidney of #14P18 on POD 154 (B-a: H&E and B-b PAS, low magnification, bar: 500 μm). (C) Photo of MMF crystallization in #14P66 SVC (C-a). Photo Of #14P66’s excised graft kidney (C-b). The color of the excised graft kidney was grossly normal. Excised graft kidney on POD 187 of #14P66 (C-c: PAS, high magnification, Bar: 100μm. C-d: HE, low magnification, Bar: 500 μm. No histologic evidence of rejection. (D) Percentage of peripheral blood macrochimerism (pig CD3 positive T cells) of #14P66 (orange line. Group B) and #14P18 (gray line, Group B) and #14P65 (blue line, Group C) following K-VTXTx. The macrochimerism of baboons in these baboons was lower than that 1615 and 2415 (F). (E) IL-6 concentration in sera of Group B (left: #14P18, right: #14P66). Either baboon showed no elevation of IL6 concentration. (F) SIRPα expression (green) in a naive pig kidney (a) and isolated podoeytes (d). (b) A merged image of SIRPα (green) and Nephrin (red) expression in the naive pig kidney, (e) Nephrin expression on isolated pig podoeytes. (c) and (f) negative controls. Bar: 50μm. (G) SIRPα expression in pig kidney grafts from long-term acceptors, 14P18 (a) and 14P66 (b) in Group B and from baboons 13P60 (c), 13P79 (d), and 14P56 (e) in Group C that developed > 2+ proteinuria, (f-j) are negative controls. Bar: 50μm
