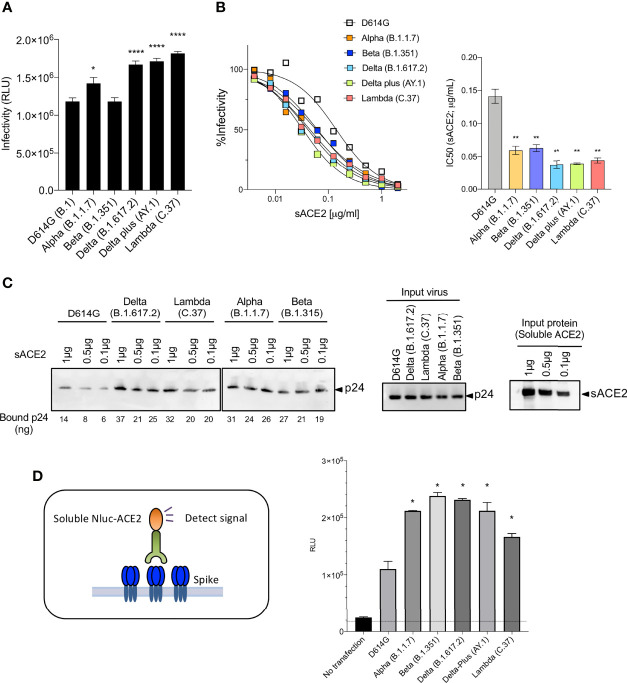
Figure 3.
Neutralization of variant spike protein pseudotyped viruses by sACE2, monoclonal antibodies and virus-ACE2 binding assay. (A) Infectivity of virus pseudotyped by variant and D614G spike proteins. Viruses were normalized for RT activity and applied to target cells. Infectivity of viruses pseudotyped with the variant spike proteins were tested on ACE2.293T. Luciferase activity was measured two days post-infection. Significance was based on two-sided t-test. (B) Neutralization of variant spike protein variants by sACE2. Viruses pseudotyped with variant spike proteins were incubated with a serially diluted recombinant sACE2 and then applied to ACE2.293T cells. Each plot represents the percent infectivity of D614G and other variant spike pseudotyped viruses. The diagram shows the IC50 for each curve. (C) Nickel beads were coated for 1 hour with 1, 0.5 and 0.1 μg of sACE2 proteins. Unbound protein was removed and SARS-CoV-2 variant pseudotyped virions (D614G, Alpha, Beta, Delta, Lambda) were incubated with the beads. After 1 hour, the bound virions were analyzed on an immunoblot with antibody p24 antibody. Beads-bound p24 (ng) was calculated and indicated in the bottom (left). Input virions were analyzed on an immunoblot with anti-p24 antibody (middle). Input sACE2 proteins were analyzed on an immunoblot with anti-His-tag antibody (right). (D) Same amount (4μg) of spike was transfected on 2x106 cells of 293T cells. Spike expressing cells were incubated with 0.2μg of sACE2-Nluc protein. After 30min of incubation, Luc activity was measured. (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ****P ≤ 0.0001).