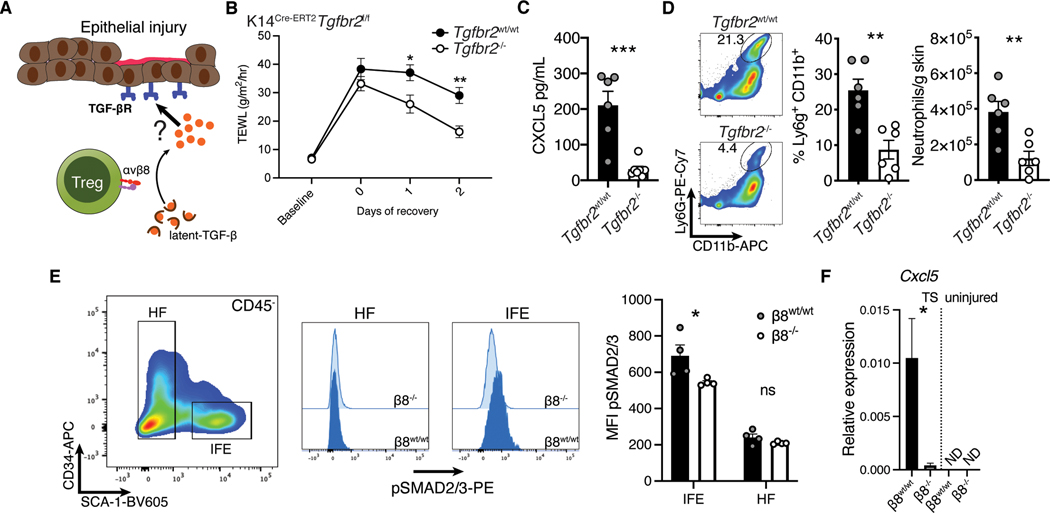
Fig. 6. TGF-β signaling in keratinocytes promoted neutrophil recruitment acutely following epidermal injury.
(A) Schematic representation of our hypothesis that during epithelial injury keratinocytes sense TGF-β activated by Tregs. While Treg intrinsic sensing of TGF-β was not important during epithelial repair, a paracrine response through a secondary cell type was possible. (B) Kinetic transepidermal water loss measurements taken before and after tape stripping K14Cre-ERT2Tgfbr2f/f mice treated with either vehicle (Tgfbr2wt/wt) or tamoxifen (Tgfbr2f/f). (C) Whole skin biopsy lysate ELISA for CXCL5. (D) Flow cytometric quantification of neutrophils in skin two days after injury. (E) Keratinocytes from Foxp3Cre-ERT2Itgb8f/f mice treated with either vehicle or tamoxifen were phenotyped by flow cytometry for SMAD2/3 phosphorylation after injury. (F) CD45−Sca-1+ epidermal cells from Treg β8wt/wt and β8−/− mice were sorted from tape stripped, or uninjured mice and analyzed for Ccxl5 expression by qPCR. Data are representative of three independent experiments, n = 4–6 mice per group; error bars are SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (B) or a unpaired two-tailed t test (C-F).