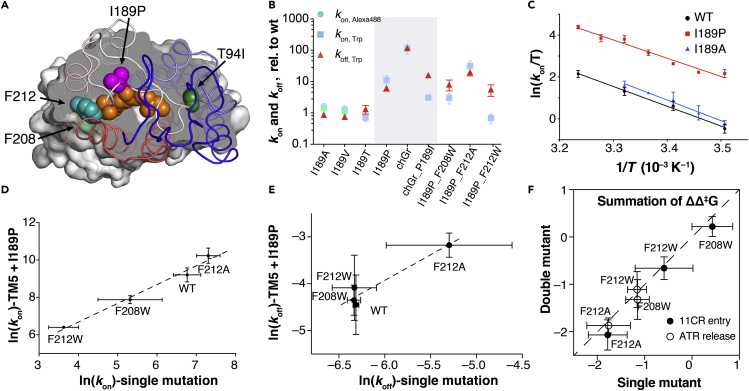
Figure 4.
Double mutant analysis reveals localized mutational effects
(A) Two TM5 sites (F208, teal; F212, lime green), I189 (magenta), and T94I (forest green) highlighted in Rho (PDB: 1U19).
(B) Mutational effect at site 189. I189P simultaneously increases the 11CR entry and ATR release kinetics (mean ± STD).
(C) The Eyring plot for I189P and I189A mutants. The kinetics (mean ± STD) were measured using the Alexa 488-based assay.
(D) Double logarithmic plot of kon (mean ± STD), Trp of TM5 single mutant versus TM5/I189P double mutants. I189P reduces the activation free energy (Δ‡G) by 1.6 ± 0.3 kcal mol−1. The fitting equation is ln(kon(I189P)) = (0.997 ± 0.093)×ln(kon(I189)) + (2.69 ± 0.55) (R2 = 0.98).
(E) Logarithmic plot of koff (mean ± STD), Trp in TM5 single mutant and TM5/I189P double mutants. I189P reduces the activation free energy (Δ‡G) by 1.6 ± 0.8 kcal mol−1. The fitting equation is ln(kon(I189P)) = (1.09 ± 0.23)×ln(kon(I189)) + (2.6 ± 1.4) (R2 = 0.92).
(F) Summation of ΔΔ‡G in single mutants vs. ΔΔ‡G in the corresponding double mutants.