FIGURE 8.
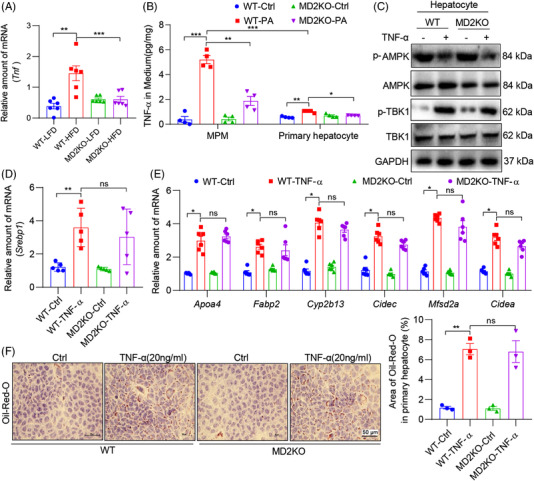
Tumour necrosis factor‐α (TNF‐α)‐α, induced by palmitate (PA) and MD2, activates TBK1 to suppress AMPK. (A) mRNA levels of Tnfa in liver tissues of WT and MD2KO mice fed a high‐fat diet (HFD) for 16 weeks (n = 6; mean ± SEM; **p < .01 and ***p < .001). (B) Mouse primary macrophages (MPM) and hepatocytes were isolated from WT and MD2KO mice. Cells were exposed to 200 μM PA for 48 h. Levels of TNF‐α protein in culture media was measured by ELISA (n = 4; mean ± SEM; **p < .01 and ***p < .001). (C) Primary hepatocytes were exposed to 20 ng/ml TNF‐α for 1 h. Levels of p‐AMPK and p‐TBK1 were detected by immunoblotting. GAPDH was used as loading control. (D) mRNA levels of Srebp1 in primary hepatocytes from WT and MD2KO mice that were exposed to 20 ng/ml TNF‐α for 48 h (n = 4; mean ± SEM; ns, not significant; **p < .01). (E) mRNA levels of sterol regulatory element binding protein 1 (SREBP1) target genes in cells treated as indicated in panel (D) (n = 6; mean ± SEM; ns, not significant; *p < .05). (F) Oil red O staining of cells exposed to TNF‐α (scale bar = 50 μm). Cells were treated as indicated in panel (D). Quantification of lipid area is shown in right panel (n = 3; mean ± SEM; ns, not significant; *p < .05)
