Figure 4. PUS7 activity is sufficient to drive molecular findings in HeLa cells.
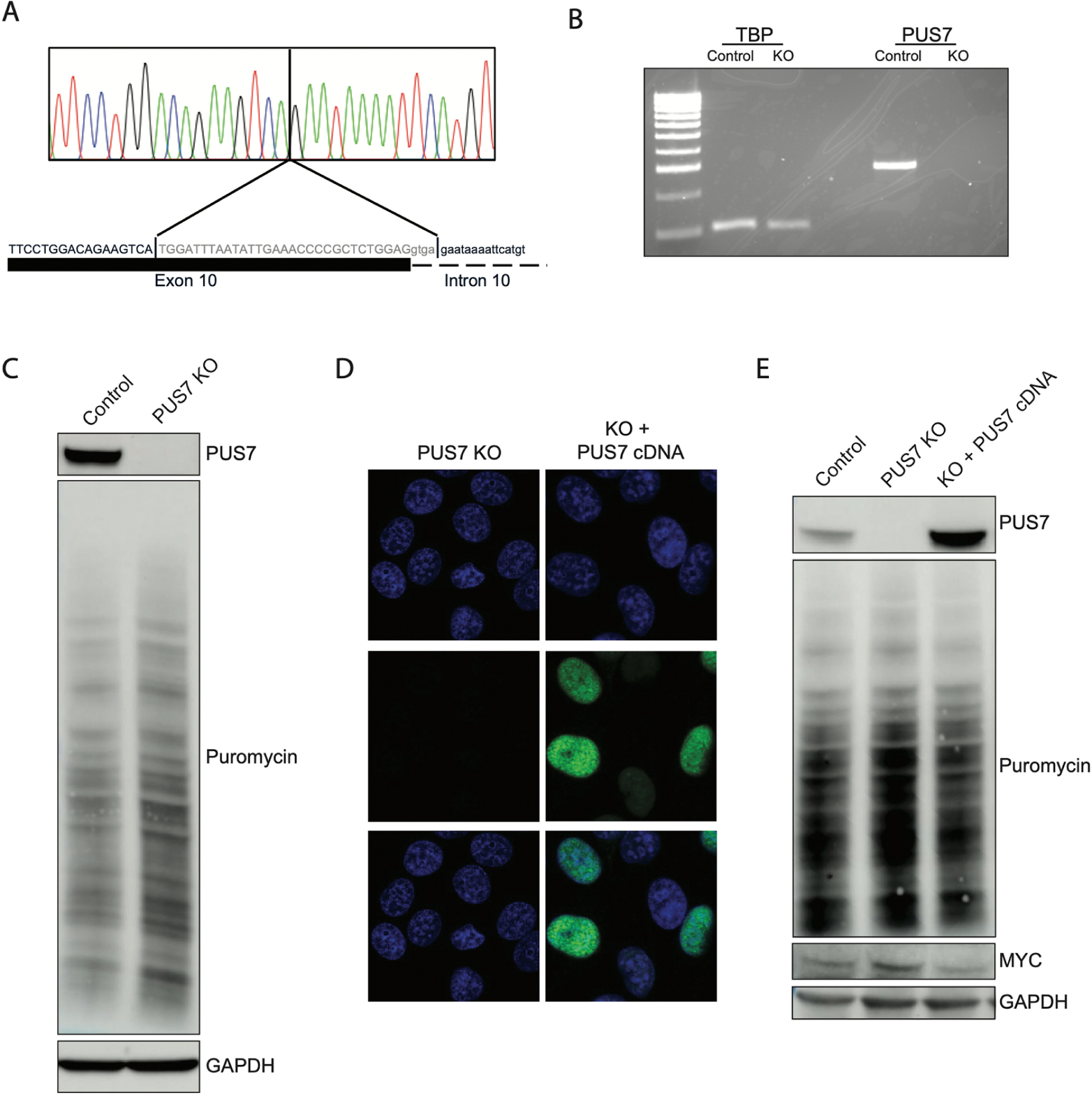
A) Sanger sequencing of genomic DNA extracted from CRISPR induced PUS7 knockout in HeLa cells demonstrates cells are homozygous for a 34 bp deletion at the 3’ end of exon 10 extending into intron 10. B) RT-PCR from total RNA extracted from PUS7 KO cells demonstrating KO cells have no detectable PUS7 mRNA. C) Western blot of whole cell lysates from KO cells demonstrating that cells do not generate detectable stable protein and that protein translation is increased in KO cells. D) Immunocytochemistry of HeLa and KO cells demonstrates lack of PUS7 protein in KO cells. Transient transfection with plasmid expressing PUS7 cDNA demonstrates that expressed protein localizes to the nucleus. Top row: DAPI only, Middle row: anti-PUS7 IHC, Bottom row: merge E) Western blot of whole cell lysates purified from KO cells transiently transfected with PUS7 expression plasmid demonstrates significant overexpression compared to parental HeLa cells. Plasmid expressing PUS7 cDNA is able to decrease puromycin incorporation and decrease MYC protein levels relative to untransfected KO cells.
