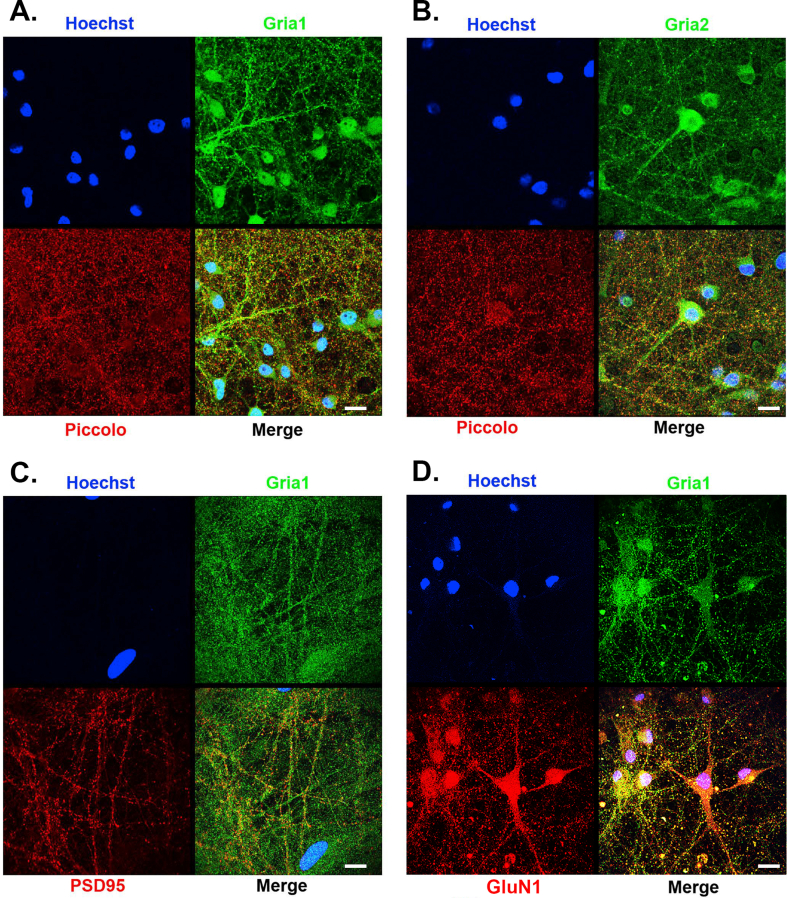
Supplemental Figure 1.
Immunocytochemically-defined pre- and post-synaptic elements indicate that there is synaptic connectivity in cortical neuron cultures. Panel A. DIV 14 cortical neuron cultures underwent immunocytochemical staining for Hoechst staining of nuclei, the Gria1 subunit of AMPA receptors (green) and the presynaptic protein, Piccolo (red). Merge image of a single confocal slice reveals pre- and post-synaptic apposition of puncta reflecting the existence of AMPA'ergic synapses. Calibration bar, 30 microns. Panel B. DIV 14 cortical neuron cultures underwent immunocytochemical staining for Hoechst staining of nuclei, the Gria2 subunit of AMPA receptors (green) and the presynaptic protein, Piccolo (red). Merge image of a single confocal slice reveals pre- and post-synaptic apposition of puncta reflecting the existence of AMPA'ergic synapses. Calibration bar, 30 microns. Panel C. DIV 14 cortical neuron cultures underwent immunocytochemical staining for Hoechst staining of nuclei, Gria1 subunit of AMPA receptors (green) and the postsynaptic density protein, PSD95 (red). Merge image of a single confocal slice reveals Gria1 puncta adjacent to PSD95 reflecting the existence of AMPA'ergic synapses. Calibration bar, 30 microns. Panel D. DIV 14 cortical neuron cultures underwent immunocytochemical staining for Hoechst staining of nuclei, the Gria1 subunit of AMPA receptors (green) and GluN1 subunit of NMDA receptors (red). Merge image of a single confocal slice reveals Gria1 puncta co-localizing with GluN1 puncta reflecting the existence of synapses containing both AMPA and NMDA receptors. Calibration bar, 30 microns.