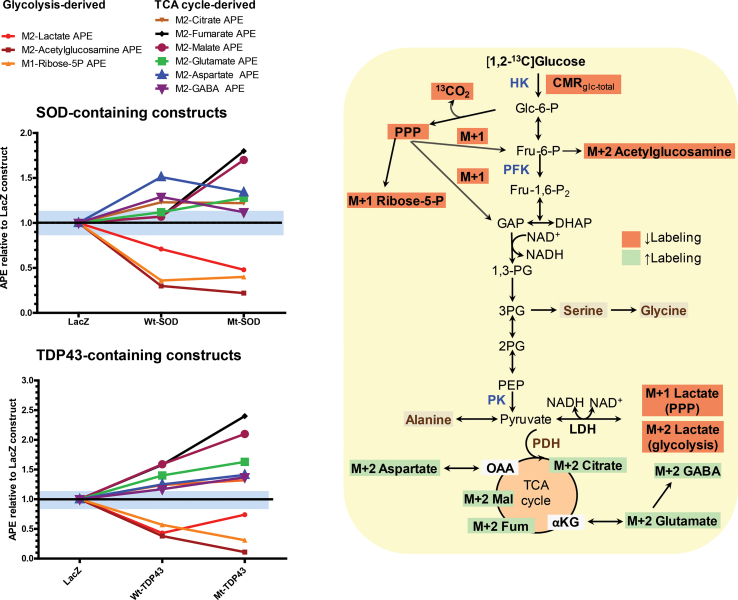
Supplemental Figure 6.
Experimental ALS causes upregulation of flux of [1,2-13C2]glucose into oxidative pathways and downregulation of glycolysis and its branch pathways. Mean values for the atom percent excess (APE, i.e., the fraction of the analyte containing 13C atoms above natural abundance; see Methods) for each metabolite were normalized to the respective values for the LacZ constructs and plotted for each experimental group. The individual and mean values for each experimental group and statistical differences among groups are presented in Figure 2, Figure 3 of the main text. The blue shaded area represents ± mean 95% confidence interval (CI) that was calculated from the 95% CIs for all compounds in the LacZ constructs. Metabolites produced by (i.e., lactate) or derived from branch pathways (i.e., ribose-5-phosphate (P) and acetylglucosamine) of the glycolytic pathway (pathways are illustrated in the right panel) have reduced enrichment from [1,2-13C2]glucose in the Wt and Mt Cu++/Zn++ superoxide dismutase (SOD1) (top left panel) and TAR DNA binding protein of 43 kDa molecular weight (TDP43) (bottom left panel) constructs compared with LacZ constructs. In contrast, metabolites that are components of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle (fumarate (Fum), malate (Mal), and citrate (Cit)) and amino acids derived from the TCA cycle (aspartate, glutamate, and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)) have increased enrichment compared with the LacZ construct. Other abbreviations: M + 1 or M + 2, mass of the compound containing 1 or 2 13C atoms derived from [1,2-13C2]glucose, respectively; HK, hexokinase; Glc-6-P, glucose-6-P; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; Fru-6-P, fructose-6-P; PFK, phosphofructo-1-kinase; Fru-1,6-P2, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; GAP, glyceraldehyde-3-P; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone-P; 1,3-PG, 1,3-diphosphoglycerate; 3PG, 3-phosphoglycerate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PK, pyruvate kinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; OAA, oxaloacetate; ∝- KG, ∝-ketoglutarate.